DNA replication origin function is promoted by H3K4 di-methylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 22851644
- PMCID: PMC3454870
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.112.142349
DNA replication origin function is promoted by H3K4 di-methylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
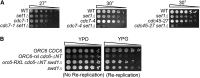
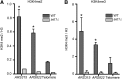
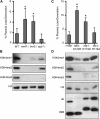
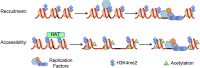
DNA replication is a highly regulated process that is initiated from replication origins, but the elements of chromatin structure that contribute to origin activity have not been fully elucidated. To identify histone post-translational modifications important for DNA replication, we initiated a genetic screen to identify interactions between genes encoding chromatin-modifying enzymes and those encoding proteins required for origin function in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We found that enzymes required for histone H3K4 methylation, both the histone methyltransferase Set1 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Bre1, are required for robust growth of several hypomorphic replication mutants, including cdc6-1. Consistent with a role for these enzymes in DNA replication, we found that both Set1 and Bre1 are required for efficient minichromosome maintenance. These phenotypes are recapitulated in yeast strains bearing mutations in the histone substrates (H3K4 and H2BK123). Set1 functions as part of the COMPASS complex to mono-, di-, and tri-methylate H3K4. By analyzing strains lacking specific COMPASS complex members or containing H2B mutations that differentially affect H3K4 methylation states, we determined that these replication defects were due to loss of H3K4 di-methylation. Furthermore, histone H3K4 di-methylation is enriched at chromosomal origins. These data suggest that H3K4 di-methylation is necessary and sufficient for normal origin function. We propose that histone H3K4 di-methylation functions in concert with other histone post-translational modifications to support robust genome duplication.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

