Consensus guidelines for the prevention and treatment of catheter-related infections and peritonitis in pediatric patients receiving peritoneal dialysis: 2012 update
- PMID: 22851742
- PMCID: PMC3524923
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00091
Consensus guidelines for the prevention and treatment of catheter-related infections and peritonitis in pediatric patients receiving peritoneal dialysis: 2012 update
Figures


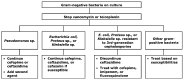
References
-
- Auron A, Simon S, Andrews W, Jones L, Johnson S, Musharaf G, et al. Prevention of peritonitis in children receiving peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 2007; 22:578–85 - PubMed
-
- The EMMES Corporation North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies: NAPRTCS 2008 Annual Report. Renal Transplantation, Dialysis, Chronic Renal Insufficiency. Rockville, MD: The EMMES Corporation; 2008. [Available online at: https://web.emmes.com/study/ped/annlrept/Annual%20Report%20-2008.pdf; accessed April 2012]
-
- Warady BA, Schaefer F, Holloway M, Alexander S, Kandert M, Piraino B, et al. Consensus guidelines for the treatment of peritonitis in pediatric patients receiving peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 2000; 20:610–24 - PubMed
-
- Warady BA, Feneberg R, Verrina E, Flynn JT, Müller–Wiefel DE, Besbas N, et al. Peritonitis in children who receive long-term dialysis: a prospective evaluation of therapeutic guidelines. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 18:2172–9 - PubMed
-
- Schaefer F, Feneberg R, Aksu N, Donmez O, Sadikoglu B, Alexander SR, et al. Worldwide variation of dialysis-associated peritonitis in children. Kidney Int 2007; 72:1374–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

