The SNPforID Assay as a Supplementary Method in Kinship and Trace Analysis
- PMID: 22851934
- PMCID: PMC3375134
- DOI: 10.1159/000338855
The SNPforID Assay as a Supplementary Method in Kinship and Trace Analysis
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Short tandem repeat (STR) analysis using commercial multiplex PCR kits is the method of choice for kinship testing and trace analysis. However, under certain circumstances (deficiency testing, mutations, minute DNA amounts), STRs alone may not suffice. METHODS: We present a 50-plex single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assay based on the SNPs chosen by the SNPforID consortium as an additional method for paternity and for trace analysis. The new assay was applied to selected routine paternity and trace cases from our laboratory. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS: Our investigation shows that the new SNP multiplex assay is a valuable method to supplement STR analysis, and is a powerful means to solve complicated genetic analyses.
Hintergrund: In der modernen Vaterschafts-und Spurenanalytik ist die Untersuchung sogenannter Short Tandem Repeats (STRs) heute das Mittel der Wahl. In bestimmten Fällen (Defizienzen, Mutationen in den STR-Systemen, sehr geringe DNA-Mengen) kann die STR-Analyse allein unter Umständen zur Klärung nicht ausreichen.
Methoden: Wir stellen als zusätzliche Methode einen von uns auf Basis der vom SNPforID-Konsortium vorgeschlagenen Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) entwickelten, 50 SNPs umfassenden Assay vor. Dieser neue Multiplex-Assay wurde in verschiedenen Routinefällen angewandt.
Ergebnisse und Schlussfolgerungen: Unsere Untersuchungen zeigen, dass die SNP-Analyse eine wertvolle Ergänzung der STR-Untersuchung darstellt und geeignet ist, zur Lösung komplizierter Spuren-und Vaterschaftsfälle eingesetzt zu werden.
Figures

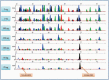
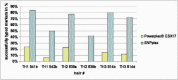
References
-
- Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V, Thein SL. Individual-specific ‘fingerprints’ of human DNA. Nature. 1985;316:76–79. - PubMed
-
- Jeffreys AJ, Wilson V, Thein SL. Hypervariable ‘minisatellite’ regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985;314:673–73. - PubMed
-
- Mullis K, Faloona F, Scharf S, Saiki R, Horn G, Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Hagelberg E, Gray IC, Jeffreys AJ. Identification of the skeletal remains of a murder victim by DNA analysis. Nature. 1991;352:427–429. - PubMed
-
- Jeffreys AJ, Allen MJ, Hagelberg E, Sonnberg A. Identification of the skeletal remains of Josef Mengele by DNA analysis. Forensic Sci Int. 1992;56:65–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

