Kinship Analysis with Diallelic SNPs - Experiences with the SNPforID Multiplex in an ISO17025 Accreditated Laboratory
- PMID: 22851935
- PMCID: PMC3375138
- DOI: 10.1159/000338957
Kinship Analysis with Diallelic SNPs - Experiences with the SNPforID Multiplex in an ISO17025 Accreditated Laboratory
Abstract
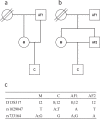
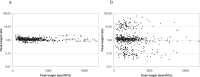
BACKGROUND: The mutation rate of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) is estimated to be 100,000 times lower than that of short tandem repeats (STRs), which makes SNPs very suitable for relationship testing. The SNPforID multiplex assay was the first SNP typing assay that was a real alternative to the commonly used STR kits in kinship and crime case work and the first SNP assay to be validated in a forensic laboratory accredited according to the ISO17025 standard. METHODS: A total of 54 crime case samples were typed with the SNPforID multiplex assay. 30 samples from relationship cases were sequenced in selected SNP loci. RESULTS: It was demonstrated that mixtures were easily detected with the SNPforID assay by analyzing the signal strengths of the detected alleles. Unusual imbalances in signal strengths that were observed in a few individuals could be explained by unexpected SNPs in one of the primer binding sites. A complicated relationship case with four closely related individuals is presented. CONCLUSION: Mixtures can be detected with bi-allelic SNPs. The SNPforID assay is a very useful supplement to the STR kits in relationship testing.
Hintergrund: Die Mutationsrate von Single-Nucleotide-Polymorphismen (SNPs) ist 100 000 Mal niedriger als die Mutationsrate von Short-Tandem-Repeats (STRs). Die kleine Mutationsrate macht SNPs sehr nützlich für die Abstammungsbegutachtung. Der SNPforID-Multiplex war der erste SNP-Typisierungstest, der eine gute Ergänzung und vielleicht ein echte Alternative zu STR-Kits in der Abstammungsbegutachtung war, und der erste forensische SNP-Test, der nach dem ISO17025-Standard akkreditiert worden ist.
Methoden: Insgesamt 54 Proben von Kriminalfällen wurden mit dem SNPforID-Multiplex-Test untersucht. Weiterhin wurden 30 Proben von Abstammungsfällen in ausgewählten SNP-Loci sequenziert.
Ergebnisse: Es wurde gezeigt, dass DNA-Mischungen leicht mit dem SNPforID-Test durch die Analyse der Signalstärke der detektierten Allele erkannt werden konnten. Ungewöhnliche Ungleichgewichte in SNP-Signal-stärken in einigen Proben konnten durch zusätzliche/unerwartete SNPs in einer der Primer-Bindungsstellen erklärt werden. Ein komplizierter Abstammungsfall mit vier eng verwandten Individuen wird als Beispiel vorgestellt.
Schlussfolgerung: DNA-Mischungen können mit bi-alleli-schen SNPs erkannt werden. Der SNPforID-Test ist eine sehr nützliche/wertvolle Ergänzung zu STR-Kits in der Abstammungsbegutachtung.
Figures
References
-
- Sanchez JJ, Phillips C, Børsting C, Balogh K, Bogus M, Fondevilla M, Harrison CD, Musgrave-Brown E, Salas A, Syndercombe-Court D, Schneider PM, Carracedo A, Morling N. A multiplex assay with 52 single nucleotide polymorphisms for human identification. Electrophoresis. 2006;27:1713–1724. - PubMed
-
- Musgrave-Brown E, Ballard D, Balogh K, Bender K, Berger B, Bogus M, Børsting C, Brion M, Fondevila M, Harrison C, Oguzturun C, Parson W, Phillips C, Proff C, Ramos-Luis E, Sanchez JJ, Diz PS, Rey B, Stradmann-Bellinghausen B, Thacker C, Carracedo A, Morling N, Scheithauer R, Schneider PM, Court DS. Forensic validation of the SNPforID 52-plex assay. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2007;1:186–190. - PubMed
-
- Phillips C, Fondevila M, García-Magarinos M, Rodriguez A, Salas A, Carrecedo A, Lareu MV. Resolving relationship tests that show ambiguous STR results using autosomal SNPs as supplementary markers. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2008;2:198–204. - PubMed
-
- Lou C, Cong B, Li S, Fu L, Zhang X, Feng T, Su S, Ma C, Yu F, Ye J, Pei L. A SNaPshot assay for genotyping 44 individual identification single nucleotides polymorphisms. Electrophoresis. 2011;32:368–378. - PubMed
-
- Tomas C, Axler-DiPerte G, Budimlija ZM, Børsting C, Coble MD, Decker AE, Eisenberg A, Fang R, Fondevila M, Fredslund SF, Gonzalez S, Hansen AJ, Hoff-Olsen P, Haas C, Kohler P, Kriegel AK, Lindblom B, Manohar F, Maroñas O, Mogensen HS, Neureuther K, Nilsson H, Scheible MK, Schneider PM, Sonntag ML, Stangegaard M, Syndercombe-Court D, Thacker CR, Vallone PM, Westen AA, Morling N. Autosomal SNP typing of forensic samples with the GenPlex(tm) HID System: Results of a collaborative study. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2011;5:369–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

