Detection of M-sequences from spike sequence in neuronal networks
- PMID: 22851966
- PMCID: PMC3407601
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/862579
Detection of M-sequences from spike sequence in neuronal networks
Abstract
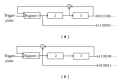
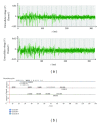
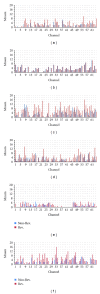
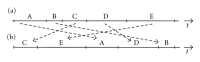
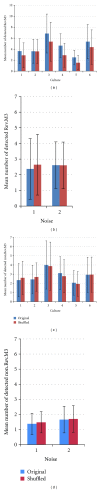
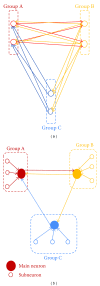
In circuit theory, it is well known that a linear feedback shift register (LFSR) circuit generates pseudorandom bit sequences (PRBS), including an M-sequence with the maximum period of length. In this study, we tried to detect M-sequences known as a pseudorandom sequence generated by the LFSR circuit from time series patterns of stimulated action potentials. Stimulated action potentials were recorded from dissociated cultures of hippocampal neurons grown on a multielectrode array. We could find several M-sequences from a 3-stage LFSR circuit (M3). These results show the possibility of assembling LFSR circuits or its equivalent ones in a neuronal network. However, since the M3 pattern was composed of only four spike intervals, the possibility of an accidental detection was not zero. Then, we detected M-sequences from random spike sequences which were not generated from an LFSR circuit and compare the result with the number of M-sequences from the originally observed raster data. As a result, a significant difference was confirmed: a greater number of "0-1" reversed the 3-stage M-sequences occurred than would have accidentally be detected. This result suggests that some LFSR equivalent circuits are assembled in neuronal networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spike Code Flow in Cultured Neuronal Networks.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016;2016:7267691. doi: 10.1155/2016/7267691. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27217825 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous activity and recurrent inhibition in cultured hippocampal networks.Synapse. 1993 Jul;14(3):206-13. doi: 10.1002/syn.890140304. Synapse. 1993. PMID: 8211707
-
Complex spike patterns in olfactory bulb neuronal networks.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Jan 15;239:11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Sep 26. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25256643
-
Decoupling through synchrony in neuronal circuits with propagation delays.Neuron. 2008 Apr 10;58(1):118-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.036. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18400168
-
A metric for space.Hippocampus. 2008;18(12):1142-56. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20483. Hippocampus. 2008. PMID: 19021254 Review.
Cited by
-
Learning process for identifying different types of communication via repetitive stimulation: feasibility study in a cultured neuronal network.AIMS Neurosci. 2019 Oct 16;6(4):240-249. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2019.4.240. eCollection 2019. AIMS Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 32341980 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of correlating adjacent neurons for identifying communications: Feasibility experiment in a cultured neuronal network.AIMS Neurosci. 2017 Dec 25;5(1):18-31. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2018.1.18. eCollection 2018. AIMS Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 32341949 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation of Code Spectrum and Code Flow of Cultured Neuronal Networks.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016;2016:7186092. doi: 10.1155/2016/7186092. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27239189 Free PMC article.
-
Spike Code Flow in Cultured Neuronal Networks.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016;2016:7267691. doi: 10.1155/2016/7267691. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27217825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonifazi P, Goldin M, Picardo MA, et al. GABAergic hub neurons orchestrate synchrony in developing hippocampal networks. Science . 2009;326(5958):1419–1424. - PubMed
-
- Lecerf C. The double loop as a model of a learning neural system. Proceedings of the World Multiconference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics (SCI '98); 1998; pp. 587–594.
-
- Choe Y. Analogical cascade: a theory on the role of the thalamo-cortical loop in brain function. Neurocomputing . 2003;52–54:713–719.
-
- Tamura S, Mizuno-Matsumoto Y, Chen YW, Nakamura K. Association and abstraction on neural circuit loop and coding. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing (IIH-MSP '09); September 2009; IEEE Computer Society; pp. 414–417.
-
- Thorpe S, Fize D, Marlot C. Speed of processing in the human visual system. Nature . 1996;381(6582):520–522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

