Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Arabic-Speaking Countries
- PMID: 22851968
- PMCID: PMC3407623
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/902873
Type II Diabetes Mellitus in Arabic-Speaking Countries
Abstract
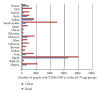
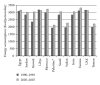
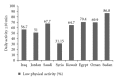
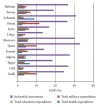
The global epidemic of diabetes has not spared the Arabic-speaking countries, which have some of the highest prevalence of type II diabetes. This is particularly true of the Arab Gulf, a conglomerate of high income, oil-producing countries where prevalence rates are the highest. The prevalence rates among adults of the Arabic speaking countries as a whole range between 4%-21%, with the lowest being in Somalia and the highest in Kuwait. As economic growth has accelerated, so has the movement of the populations to urban centers where people are more likely to adopt lifestyles that embrace increased high-calorie food consumption and sedentary lifestyles. These factors likely contribute to the increased prevalence of obesity and diabetes in the Arabic speaking countries.
Figures
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance WorldHealthorganization. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. WHO, 1999, . http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1999/WHO_NCD_NCS_99.2.pdf.
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 5th edition. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2011. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas. - PubMed
-
- Roglic G, Unwin N. Mortality attributable to diabetes: estimates for the year 2010. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2010;87(1):15–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

