Strain of experimental animals and modulation of nitric oxide pathway: their influence on development of renal failure in an experimental model of hepatorenal syndrome
- PMID: 22852015
- PMCID: PMC3400905
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2012.29281
Strain of experimental animals and modulation of nitric oxide pathway: their influence on development of renal failure in an experimental model of hepatorenal syndrome
Abstract
Introduction: Pathomechanism of HRS is still poorly understood. The aim of our study was: (1) to test whether different strains of rats could develop typical HRS, and (2) to estimate the influence of activation and inhibition of nitric oxide for development of renal failure in course of HRS.
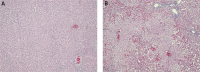
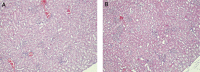
Material and methods: First, we used 16 of Wistar and 16 of Sprague-Dawley rats in galactosamine model of HRS. Next, we used 48 of SDR rats, which received saline, N-nitro-L-arginine or L-arginine before and after liver damage. Twenty four hours urine and blood samples were collected 48 h after saline or Ga1N injection. Biochemical parameters were determined in serum or urine and then creatinine clearance and osmolality clearance were calculated. Liver and kidney tissues were collected for histopathological examination.
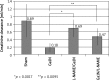
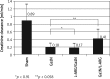
Results: Liver failure developed in all tested groups with significant increase of bilirubin (p < 0.001), ALT (p < 0.001) and ammonia (p < 0.001). Nevertheless we did not achieve any evidence of renal failure in Wistar, but we found typical renal failure in Sprague-Dawley group with significant decrease in creatinine clearance (p < 0.0012) and increase in concentration of creatinine and urea (p < 0.001) and (p < 0.001) respectively. Inhibition of NOS prevented development of renal failure with significant improvement of GFR both before (p < 0.0017) and after (p < 0.003) Ga1N injection. Injection of L-arginine after Ga1N injection did not caused significant improvement of GFR.
Conclusions: Our study showed, that genetic factors might be responsible for development of renal failure in course of HRS and nitric oxide play important role in acute model of this syndrome.
Keywords: experimental studies; hepatorenal syndrome; nitric oxide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of nitric oxide pathway regulation on water/sodium balance and renal function in a rodent model of acute liver and renal failure.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Sep 27;20:1735-44. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890757. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25270512 Free PMC article.
-
[Role of nitric oxide system in pathogenesis of experimental model of hepatorenal syndrome].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Apr;24(142):293-7. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 18634358 Polish.
-
[Race of experimental animals and development of renal failure in animal model of hepatorenal syndrome].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Apr;24(142):298-302. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 18634359 Polish.
-
[Description of an experimental model of hepatorenal syndrome in Wistar rats].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004 Aug;17(98):119-22. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2004. PMID: 15603319 Polish.
-
New Developments in Hepatorenal Syndrome.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Feb;16(2):162-177.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.05.041. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 28602971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
D-Galactosamine Intoxication in Experimental Animals: Is it Only an Experimental Model of Acute Liver Failure?Med Sci Monit. 2015 May 22;21:1469-77. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893291. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26009004 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of the Third Generation Vasodilatory Βeta - Blocker Nebivolol against D-Galactosamine - Induced Hepatorenal Syndrome in Rats.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017 Dec 13;5(7):880-892. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.173. eCollection 2017 Dec 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29362613 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nitric Oxide Pathway in Development and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in Rats Sensitive and Resistant to its Occurrence in an Experimental Model of 5/6 Nephrectomy.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Oct 11;23:4865-4873. doi: 10.12659/msm.903820. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 29018182 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nitric oxide pathway regulation on water/sodium balance and renal function in a rodent model of acute liver and renal failure.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Sep 27;20:1735-44. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890757. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25270512 Free PMC article.
-
Concerted regulation of renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate by renal dopamine and NOS I in rats on high salt intake.Physiol Rep. 2017 Mar;5(6):e13202. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13202. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28351967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong F, Nadim MK, Kellum JA, et al. Working Party proposal for a revised classification system of renal dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis. Gut. 2011;60:702–9. - PubMed
-
- Cárdenas A, Ginès P. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: the kidneys. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2011;17:184–9. - PubMed
-
- Venkat D, Venkat KK. Hepatorenal syndrome. South Med J. 2010;103:654–61. - PubMed
-
- Sussman AN, Boyer TD. Management of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13:17–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
