Medical errors - not only patients' problem
- PMID: 22852017
- PMCID: PMC3400923
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2012.29413
Medical errors - not only patients' problem
Abstract
Introduction: Medical error is often a traumatic experience not only for patients but also for doctors. However, patients as victims get much more publicity than those responsible for actual errors. The authors of the study conducted research to learn about Polish doctors' opinions on and reactions to medical errors and how they affect their further professional activity and psychological status. The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of involvement in medical errors of doctors of different specialties and different age.
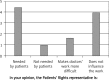
Material and methods: The research was conducted in a group of 100 doctors of different specialties. Respondents anonymously completed an experimental survey comprising 6 groups of multiple choice questions concerning such issues as awareness of the nature of medical error, legal liability of the perpetrator, consequences of medical error for further professional activity, the function of the Patients' Rights Representative and consequences of publishing the problem.
Results: The results indicate many negative effects of medical errors on physicians, such as common fear of making an error (82%), increased caution (52%), disadvantageous security measures while performing one's duties (57%), worsening of doctor-patient relations (67%), loss of social trust (62%) and increased treatment costs (40%). Forty five percent of the surveyed doctors declared that patients need the Patients' Rights Representative and 39% claimed it does not affect their work.
Conclusions: Given the significant burden on physicians' health, well-being and performance associated with medical errors, health care institutions should take this into account and provide physicians with formal systems of support.
Keywords: emotional distress; medical error; physicians; professional support.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medical errors: patients' opinion, lawyers' standpoint, medical doctrine and practice of the european court of human rights.Wiad Lek. 2019;72(12 cz 2):2416-2420. Wiad Lek. 2019. PMID: 32124762
-
Patients' and physicians' attitudes regarding the disclosure of medical errors.JAMA. 2003 Feb 26;289(8):1001-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.8.1001. JAMA. 2003. PMID: 12597752
-
[A survey on some Italian doctors' opinions about errors in clinical medicine].Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006;42(3):348-64. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006. PMID: 17124359 Italian.
-
Subtracting insult from injury: addressing cultural expectations in the disclosure of medical error.J Med Ethics. 2005 Feb;31(2):106-8. doi: 10.1136/jme.2003.005538. J Med Ethics. 2005. PMID: 15681676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Are schizophrenic patients being told their diagnosis today in France?].Encephale. 2017 Apr;43(2):160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.01.011. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27372353 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The relationship between resident burnout and safety-related and acceptability-related quality of healthcare: a systematic literature review.BMC Med Educ. 2017 Nov 9;17(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12909-017-1040-y. BMC Med Educ. 2017. PMID: 29121895 Free PMC article.
-
Medication Safety: A Need to Relook at Double-Checking Medicines?Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2019 Jul-Sep;6(3):246-252. doi: 10.4103/apjon.apjon_2_19. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31259220 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Burnout in the Association between Work-Related Factors and Perceived Errors in Clinical Practice among Spanish Residents.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 6;18(9):4931. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094931. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34066327 Free PMC article.
-
Error Disclosure Algorithms: How to Disclose Colleague's Medical Error at Individual and Organizational Levels.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021 Dec 8;35:163. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.35.163. eCollection 2021. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021. PMID: 35465170 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive biases associated with medical decisions: a systematic review.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2016 Nov 3;16(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12911-016-0377-1. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2016. PMID: 27809908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cox PM, Jr, D'Amato S, Tillotson DJ. Reducing medication errors. Am J Med Qual. 2001;16:81–6. - PubMed
-
- Pape TM, Guerra DM, Muzquiz M, et al. Innovative approaches to reducing nurses' distractions during medication administration. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2005;36:108–16. - PubMed
-
- Waterman AD, Garbutt J, Hazel E, et al. The emotional impact of medical errors on practicing physicians in the United States and Canada. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2007;33:467–76. - PubMed
-
- Spickard A, Gabbe SG, Christensen JF. Before burnout: how physicians can defuse stress. JAMA. 2002;288:1447–50. - PubMed
-
- Waterman A. Impact of medical errors on physicians by Christopher Guadagnino. 2007. Oct, available at: www.physiciansnews.com.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
