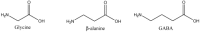Ergogenic effects of β-alanine and carnosine: proposed future research to quantify their efficacy
- PMID: 22852051
- PMCID: PMC3407982
- DOI: 10.3390/nu4070585
Ergogenic effects of β-alanine and carnosine: proposed future research to quantify their efficacy
Abstract
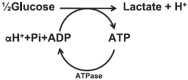
β-alanine is an amino acid that, when combined with histidine, forms the dipeptide carnosine within skeletal muscle. Carnosine and β-alanine each have multiple purposes within the human body; this review focuses on their roles as ergogenic aids to exercise performance and suggests how to best quantify the former's merits as a buffer. Carnosine normally makes a small contribution to a cell's total buffer capacity; yet β-alanine supplementation raises intracellular carnosine concentrations that in turn improve a muscle's ability to buffer protons. Numerous studies assessed the impact of oral β-alanine intake on muscle carnosine levels and exercise performance. β-alanine may best act as an ergogenic aid when metabolic acidosis is the primary factor for compromised exercise performance. Blood lactate kinetics, whereby the concentration of the metabolite is measured as it enters and leaves the vasculature over time, affords the best opportunity to assess the merits of β-alanine supplementation's ergogenic effect. Optimal β-alanine dosages have not been determined for persons of different ages, genders and nutritional/health conditions. Doses as high as 6.4 g day(-1), for ten weeks have been administered to healthy subjects. Paraesthesia is to date the only side effect from oral β-alanine ingestion. The severity and duration of paraesthesia episodes are dose-dependent. It may be unwise for persons with a history of paraesthesia to ingest β-alanine. As for any supplement, caution should be exercised with β-alanine supplementation.
Keywords: amino acid; carnosine; dietary supplement; paraesthesia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Muscle carnosine metabolism and beta-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training.Sports Med. 2010 Mar 1;40(3):247-63. doi: 10.2165/11530310-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2010. PMID: 20199122 Review.
-
Role of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine and exercise performance.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010 Jun;42(6):1162-73. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181c74e38. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010. PMID: 20479615 Review.
-
Doubling of muscle carnosine concentration does not improve laboratory 1-hr cycling time-trial performance.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2014 Jun;24(3):315-24. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2013-0125. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2014. PMID: 24457999 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of β-alanine as an ergogenic aid.Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2013;75:99-108. doi: 10.1159/000345825. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2013. PMID: 23765354
-
β-Alanine supplementation elevates intramuscular carnosine content and attenuates fatigue in men and women similarly but does not change muscle l-histidine content.Nutr Res. 2017 Dec;48:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 7. Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 29246277 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Pyruvate accumulation may contribute to acceleration-induced impairment of physical and cognitive abilities: an experimental study.Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR20204284. doi: 10.1042/BSR20204284. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33782696 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Carnosine Supplementation on Musculoskeletal Health in Adults with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 15;16(24):4328. doi: 10.3390/nu16244328. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The emerging role of protein L-lactylation in metabolic regulation and cell signalling.Nat Metab. 2025 Apr;7(4):647-664. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01259-0. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Nat Metab. 2025. PMID: 40175761 Review.
-
Space Flight Diet-Induced Deficiency and Response to Gravity-Free Resistive Exercise.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 11;12(8):2400. doi: 10.3390/nu12082400. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32796546 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Running Wheel Activity and Dietary HMB and β-alanine Co-Supplementation on Muscle Quality in Aged Male Rats.J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(5):554-561. doi: 10.1007/s12603-016-0810-2. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017. PMID: 28448086
References
-
- Artoli G.G., Gualano B., Smith A., Stout J., Lancha A.H. Role of β-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine and exercise performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009;42:1162–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials