Angiogenic signalling pathways altered in gliomas: selection mechanisms for more aggressive neoplastic subpopulations with invasive phenotype
- PMID: 22852079
- PMCID: PMC3407647
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/597915
Angiogenic signalling pathways altered in gliomas: selection mechanisms for more aggressive neoplastic subpopulations with invasive phenotype
Abstract
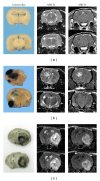
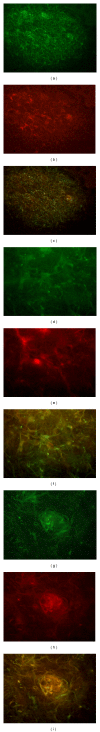
The angiogenesis process is a key event for glioma survival, malignancy and growth. The start of angiogenesis is mediated by a cascade of intratumoural events: alteration of the microvasculature network; a hypoxic microenvironment; adaptation of neoplastic cells and synthesis of pro-angiogenic factors. Due to a chaotic blood flow, a consequence of an aberrant microvasculature, tissue hypoxia phenomena are induced. Hypoxia inducible factor 1 is a major regulator in glioma invasiveness and angiogenesis. Clones of neoplastic cells with stem cell characteristics are selected by HIF-1. These cells, called "glioma stem cells" induce the synthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor. This factor is a pivotal mediator of angiogenesis. To elucidate the role of these angiogenic mediators during glioma growth, we have used a rat endogenous glioma model. Gliomas induced by prenatal ENU administration allowed us to study angiogenic events from early to advanced tumour stages. Events such as microvascular aberrations, hypoxia, GSC selection and VEGF synthesis may be studied in depth. Our data showed that for the treatment of gliomas, developing anti-angiogenic therapies could be aimed at GSCs, HIF-1 or VEGF. The ENU-glioma model can be considered to be a useful option to check novel designs of these treatment strategies.
Figures


References
-
- Kleihues P, Burger PC, Aldape KD, et al. Glioblastoma. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Lyon, France: Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC); 2007. pp. 33–49.
-
- Bergers G, Benjamin LE. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2003;3(6):401–410. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407(6801):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J. Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature. 2000;407(6801):242–248. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nature Medicine. 2003;9(6):653–660. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

