Proteolytic Potential of the MSC Exosome Proteome: Implications for an Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Proteasome
- PMID: 22852084
- PMCID: PMC3407643
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/971907
Proteolytic Potential of the MSC Exosome Proteome: Implications for an Exosome-Mediated Delivery of Therapeutic Proteasome
Abstract
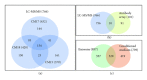
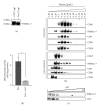
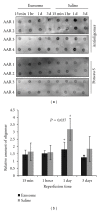
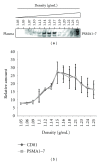
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are used in many of the current stem cell-based clinical trials and their therapeutic efficacy has increasingly been attributed to secretion of paracrine factors. We have previously demonstrated that a therapeutic constituent of this secretion is exosome, a secreted bilipid membrane vesicle of ~50-100 nm with a complex cargo that is readily internalized by H9C2 cardiomyocytes. It reduces infarct size in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R) injury. We postulate that this therapeutic efficacy is derived from the synergy of a select permutation of individual exosome components. To identify protein candidates in this permutation, the proteome was profiled and here we identified 20S proteasome as a protein candidate. Mass spectrometry analysis detected all seven α and seven β chains of the 20S proteasome, and also the three beta subunits of "immunoproteasome" with a very high confidence level. We demonstrated that a functional proteasome copurified with MSC exosomes with a density of 1.10-1.18 g/mL, and its presence correlated with a modest but significant reduction in oligomerized protein in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. Circulating proteasomes in human blood also copurified with exosomes. Therefore, 20S proteasome is a candidate exosome protein that could synergize with other constituents to ameliorate tissue damage.
Figures
References
-
- Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H, Bieback K. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294–1301. - PubMed
-
- Banas A, Teratani T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a source of human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):219–228. - PubMed
-
- In ’t Anker PS, Noort WA, Scherjon SA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in human second-trimester bone marrow, liver, lung, and spleen exhibit a similar immunophenotype but a heterogeneous multilineage differentiation potential. Haematologica. 2003;88(8):845–852. - PubMed
-
- Young HE, Steele TA, Bray RA, et al. Human reserve pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells are present in the connective tissues of skeletal muscle and dermis derived from fetal, adult, and geriatric donors. Anatomical Record. 2001;264(1):51–62. - PubMed
-
- Roubelakis MG, Pappa KI, Bitsika V, et al. Molecular and proteomic characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from amniotic fluid: comparison to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells and Development. 2007;16(6):931–952. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
