Lessons learned from the transgenic Huntington's disease rats
- PMID: 22852099
- PMCID: PMC3407652
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/682712
Lessons learned from the transgenic Huntington's disease rats
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a fatal inherited disorder leading to selective neurodegeneration and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Currently, there is no treatment to slow down or to stop the disease. There is also no therapy to effectively reduce the symptoms. In the investigation of novel therapies, different animal models of Huntington's disease, varying from insects to nonhuman primates, have been created and used. Few years ago, the first transgenic rat model of HD, carrying a truncated huntingtin cDNA fragment with 51 CAG repeats under control of the native rat huntingtin promoter, was introduced. We have been using this animal model in our research and review here our experience with the behavioural, neurophysiological, and histopathological phenotype of the transgenic Huntington's disease rats with relevant literature.
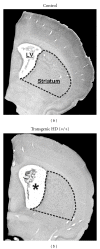
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transgenic rat model of Huntington's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2003 Mar 15;12(6):617-24. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddg075. Hum Mol Genet. 2003. PMID: 12620967
-
Transgenic mice expressing mutated full-length HD cDNA: a paradigm for locomotor changes and selective neuronal loss in Huntington's disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Jun 29;354(1386):1035-45. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0456. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10434303 Free PMC article.
-
A novel BACHD transgenic rat exhibits characteristic neuropathological features of Huntington disease.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 31;32(44):15426-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1148-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23115180 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic animal models for study of the pathogenesis of Huntington's disease and therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Apr 15;9:2179-88. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S58470. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25931812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenic Rat Models of Huntington's Disease.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015;22:135-47. doi: 10.1007/7854_2013_245. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24013873 Review.
Cited by
-
Coexistence of Gait Disturbances and Chorea in Experimental Huntington's Disease.Behav Neurol. 2015;2015:970204. doi: 10.1155/2015/970204. Epub 2015 May 6. Behav Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26063966 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Models of Huntington's Disease: An Overview.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 16;11(12):3331. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123331. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal learning and associative memory impairments in a BACHD rat model for Huntington disease.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 1;8(11):e71633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071633. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker FO. Huntington’s disease. The Lancet. 2007;369(9557):218–228. - PubMed
-
- Bonelli RM, Hofmann P. A systematic review of the treatment studies in Huntington’s disease since 1990. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 2007;8(2):141–153. - PubMed
-
- Andresen JM, Gayan J, Djousse L, et al. The relationship between CAG repeat length and age of onset differs for Huntington’s disease patients with juvenile onset or adult onset. Annals of Human Genetics. 2007;71(3):295–301. - PubMed
-
- Andrew SE, Goldberg YP, Kremer B, et al. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington’s disease. Nature Genetics. 1993;4(4):398–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

