Bio-Rad's Bio-Plex® suspension array system, xMAP technology overview
- PMID: 22852821
- PMCID: PMC3469222
- DOI: 10.3109/13813455.2012.705301
Bio-Rad's Bio-Plex® suspension array system, xMAP technology overview
Abstract
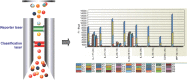
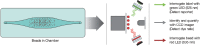
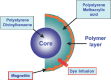
The Bio-Plex(®) system utilizes xMAP technology to permit the multiplexing of up to 100 different analytes. Multiplex analysis gives researchers the ability to look at analytes simultaneously providing more information from less sample volume in less time than traditional immunoassay methods. Similar to ELISA, xMAP utilizes an antibody sandwich for detection but differs from ELISA in capture substrate and detection method. Rather than a flat surface, Bio-Plex(®) assays make use of differentially detectable bead sets as a substrate capturing analytes in solution and employs fluorescent methods for detection. These bead sets identify the analytes and detection antibodies are used to measure the quantity of analyte. The use of differentially detectable beads enables the simultaneous identification and quantification of many analytes in the same sample.
Figures


References
-
- Engvall E, Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitive assay of immunoglobin G. Immunochemistry. 1971;8(9):871–4. - PubMed
-
- Leguin RM. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) Clin Chem. 2005;51(12):2415–18. - PubMed
-
- Van Weeman BK, Schuurs AH. Immunoassay using antigenenzyme conjugates. FEBS Lett. 1971;15(3):232–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
