Organizing pneumonia after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy of the lung
- PMID: 22853821
- PMCID: PMC3480881
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-123
Organizing pneumonia after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy of the lung
Abstract
Background: Organizing pneumonia (OP), so called bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after postoperative irradiation for breast cancer has been often reported. There is little information about OP after other radiation modalities. This cohort study investigated the clinical features and risk factors of OP after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy of the lung (SABR).
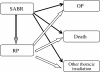
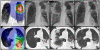
Methods: Patients undergoing SABR between 2004 and 2010 in two institutions were investigated. Blood test and chest computed tomography were performed at intervals of 1 to 3 months after SABR. The criteria for diagnosing OP were: 1) mixture of patchy and ground-glass opacity, 2) general and/or respiratory symptoms lasting for at least 2 weeks, 3) radiographic lesion in the lung volume receiving < 0.5 Gy, and 4) no evidence of a specific cause.
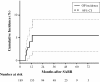
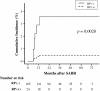
Results: Among 189 patients (164 with stage I lung cancer and 25 with single lung metastasis) analyzed, nine developed OP. The incidence at 2 years was 5.2% (95% confidence interval; 2.6-9.3%). Dyspnea were observed in all patients. Four had fever. These symptoms and pulmonary infiltration rapidly improved after corticosteroid therapy. Eight patients had presented with symptomatic radiation pneumonitis (RP) around the tumor 2 to 7 months before OP. The prior RP history was strongly associated with OP (hazard ratio 61.7; p = 0.0028) in multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: This is the first report on OP after SABR. The incidence appeared to be relatively high. The symptoms were sometimes severe, but corticosteroid therapy was effective. When patients after SABR present with unusual pneumonia, OP should be considered as a differential diagnosis, especially in patients with prior symptomatic RP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and dosimetric predictors of radiation pneumonitis in early-stage lung cancer treated with Stereotactic Ablative radiotherapy (SABR) - An analysis of UK's largest cohort of lung SABR patients.Radiother Oncol. 2021 Mar;156:153-159. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Radiother Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33333139
-
Radiation-induced organizing pneumonia after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumor.J Radiat Res. 2015 Nov;56(6):904-11. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrv049. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 26338993 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiation therapy in patients previously treated with conventional thoracic radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Nov 15;84(4):1017-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.02.020. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22543216 Free PMC article.
-
[Pulmonary damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1999 Apr 17;143(16):833-6. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1999. PMID: 10347650 Review. Dutch.
-
Post-Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia.Respir Care. 2020 May;65(5):686-692. doi: 10.4187/respcare.07150. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Respir Care. 2020. PMID: 31892515
Cited by
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy with helical TomoTherapy for medically inoperable early stage primary and second-primary non-small-cell lung neoplasm: 1-year outcome and toxicity analysis.Br J Radiol. 2015 May;88(1049):20140687. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140687. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Br J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25735428 Free PMC article.
-
A pictorial essay on radiological changes after stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung tumors.Jpn J Radiol. 2022 Jul;40(7):647-663. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01252-7. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Jpn J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35184250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia associated with radiation: A report of two cases.Oncol Lett. 2014 Feb;7(2):321-324. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1716. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24396439 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripheral lung tumors with a maximum dose of 100 Gy in five fractions and a heterogeneous dose distribution in the planning target volume.J Radiat Res. 2014 Sep;55(5):988-95. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru037. Epub 2014 May 15. J Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24833770 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Irradiation enhanced risks of hospitalised pneumonopathy in lung cancer patients: a population-based surgical cohort study.BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 27;7(9):e015022. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015022. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28963281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Crestani B, Valeyre D, Roden S. et al.Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia syndrome primed by radiation therapy to the breast. The Groupe d'Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladies Orphelines Pulmonaires (GERM"O"P) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:1929–1935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

