Redefining the impact of nutrition on breast cancer incidence: is epigenetics involved?
- PMID: 22853843
- PMCID: PMC4090752
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954422411000199
Redefining the impact of nutrition on breast cancer incidence: is epigenetics involved?
Abstract
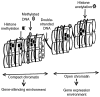
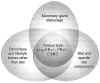
Breast cancer incidence is rising worldwide with an increase in aggressive neoplasias in young women. Possible factors involved include lifestyle changes, notably diet that is known to make an impact on gene transcription. However, among dietary factors, there is sufficient support for only greater body weight and alcohol consumption whereas numerous studies revealing an impact of specific diets and nutrients on breast cancer risk show conflicting results. Also, little information is available from middle- and low-income countries. The diversity of gene expression profiles found in breast cancers indicates that transcription control is critical for the outcome of the disease. This suggests the need for studies on nutrients that affect epigenetic mechanisms of transcription, such as DNA methylation and post-translational modifications of histones. In the present review, a new examination of the relationship between diet and breast cancer based on transcription control is proposed in light of epidemiological, animal and clinical studies. The mechanisms underlying the impact of diets on breast cancer development and factors that impede reaching clear conclusions are discussed. Understanding the interaction between nutrition and epigenetics (gene expression control via chromatin structure) is critical in light of the influence of diet during early stages of mammary gland development on breast cancer risk, suggesting a persistent effect on gene expression as shown by the influence of certain nutrients on DNA methylation. Successful development of breast cancer prevention strategies will require appropriate models, identification of biological markers for rapid assessment of preventive interventions, and coordinated worldwide research to discern the effects of diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Franco-Marina F, Lazcano-Ponce E, Lopez-Carrillo L. Breast cancer mortality in Mexico: an age–period–cohort analysis. Salud Publica Mex. 2009;51(Suppl 2):s157–s164. - PubMed
-
- Velasquez-De Charry LC, Carrasquilla G, Roca-Garavito S. Equity in access to treatment for breast cancer in Colombia (article in Spanish) Salud Publica Mex. 2009;51(Suppl 2):s246–s253. - PubMed
-
- Lozano-Ascencio R, Gomez-Dantes H, Lewis S, et al. Breast cancer trends in Latin America and the Caribbean (article in Spanish) Salud Publica Mex. 2009;51(Suppl 2):s147–s156. - PubMed
-
- Porter P. “Westernizing” women’s risks? Breast cancer in lower-income countries. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:213–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

