Properties of intermediate filament networks assembled from keratin 8 and 18 in the presence of Mg²+
- PMID: 22853896
- PMCID: PMC3403007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.06.014
Properties of intermediate filament networks assembled from keratin 8 and 18 in the presence of Mg²+
Abstract
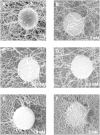
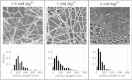
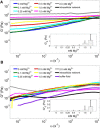
The mechanical properties of epithelial cells are modulated by structural changes in keratin intermediate filament networks. To investigate the relationship between network architecture and viscoelasticity, we assembled keratin filaments from recombinant keratin proteins 8 (K8) and 18 (K18) in the presence of divalent ions (Mg(2+)). We probed the viscoelastic modulus of the network by tracking the movement of microspheres embedded in the network during assembly, and studied the network architecture using scanning electron microscopy. Addition of Mg(2+) at physiological concentrations (<1 mM) resulted in networks whose structure was similar to that of keratin networks in epithelial cells. Moreover, the elastic moduli of networks assembled in vitro were found to be within the same magnitude as those measured in keratin networks of detergent-extracted epithelial cells. These findings suggest that Mg(2+)-induced filament cross-linking represents a valid model for studying the cytoskeletal mechanics of keratin networks.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insights into the mechanical properties of epithelial cells: the effects of shear stress on the assembly and remodeling of keratin intermediate filaments.FASEB J. 2009 Jul;23(7):2110-9. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-124453. Epub 2009 Feb 26. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19246484 Free PMC article.
-
Solo and Keratin Filaments Regulate Epithelial Tubule Morphology.Cell Struct Funct. 2018 Jun 2;43(1):95-105. doi: 10.1247/csf.18010. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Cell Struct Funct. 2018. PMID: 29709890
-
Keratin 18 overexpression but not phosphorylation or filament organization blocks mouse Mallory body formation.Hepatology. 2007 Jan;45(1):88-96. doi: 10.1002/hep.21471. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17187412
-
Revealing the Roles of Keratin 8/18-Associated Signaling Proteins Involved in the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6401. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126401. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Keratins let liver live: Mutations predispose to liver disease and crosslinking generates Mallory-Denk bodies.Hepatology. 2007 Nov;46(5):1639-49. doi: 10.1002/hep.21976. Hepatology. 2007. PMID: 17969036 Review.
Cited by
-
Active multi-point microrheology of cytoskeletal networks.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2016 Mar 24;7:484-91. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.7.42. eCollection 2016. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27335739 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale architecture: Mechanics of composite cytoskeletal networks.Biophys Rev (Melville). 2022 Aug 26;3(3):031304. doi: 10.1063/5.0099405. eCollection 2022 Sep. Biophys Rev (Melville). 2022. PMID: 38505277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermediate Filaments and the Plasma Membrane.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Jan 3;9(1):a025866. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a025866. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 28049646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Keratinase: Next Generation Green Catalyst and Prospective Applications.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 18;11:580164. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.580164. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33391200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attractive interactions among intermediate filaments determine network mechanics in vitro.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 1;9(4):e93194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093194. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24690778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrmann H., Bär H., Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:562–573. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann H., Hesse M., Magin T.M. Functional complexity of intermediate filament cytoskeletons: from structure to assembly to gene ablation. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2003;223:83–175. - PubMed
-
- Herrmann H., Aebi U. Intermediate filaments: molecular structure, assembly mechanism, and integration into functionally distinct intracellular scaffolds. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004;73:749–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

