Construction of conditional acid ceramidase knockout mice and in vivo effects on oocyte development and fertility
- PMID: 22854249
- PMCID: PMC3741991
- DOI: 10.1159/000341453
Construction of conditional acid ceramidase knockout mice and in vivo effects on oocyte development and fertility
Abstract
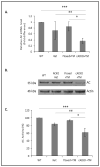
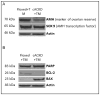
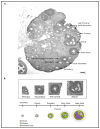
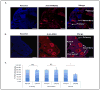
The number of resting follicles in the ovary and their successful maturation during development define the fertile female lifespan. Oocytes, enclosed within follicles, are subject to natural selection, and the majority will undergo apoptosis during prenatal life through adulthood. Our previous studies revealed high levels of the lipid hydrolase, acid ceramidase (AC), in human and mouse oocytes, follicular fluid and cumulus cells. In addition, supplementation of in vitro fertilization media with recombinant AC enhanced the survival of oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Herein we constructed and used a conditional knockout mouse model of AC deficiency (cACKO) to further investigate the role of this enzyme in oocyte survival in vivo. Immunohistochemical staining, activity assays, and western blot analysis revealed that AC expression was high in the ovaries of normal mice, particularly in the theca cells. After induction of the AC gene knockout with tamoxifen (TM), AC levels decreased in ovaries, and ceramide was correspondingly elevated. A novel immunostaining method was developed to visualize follicles at various stages, and together with light microscopic examination, the transition of the follicle from the secondary to antral stage was found to be defective in the absence of AC. Western blot analysis showed elevated BAX and PARP expression in TM-treated cACKO mouse ovaries compared to control animals. In parallel, the levels of BCL-2 and anti-Mullerian hormone, a marker of ovarian reserve, were decreased. In addition to the above, there was a significant decrease in fertility observed in the TM-treated cACKO mice. Together, these data suggest that AC plays an important role in the preservation of fertility by maintaining low ceramide levels and preventing apoptosis of theca cells, thereby promoting survival of the follicle during the transition from the secondary to antral stage.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
E.E., N.S., and E.H.S. are inventors on patents related to acid ceramidase. These patents describe the use of acid ceramidase for oocyte and embryo survival, and could in the future generate royalty income for Mount Sinai and the inventors.
Figures

References
-
- Grassmé H, Riethmüller J, Gulbins E. Biological aspects of ceramide-enriched membrane domains. Prog Lipid Res. 2007;46:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Eliyahu E, Park JH, Shtraizent N, He X, Schuchman EH. Acid ceramidase is a novel factor required for early embryo survival. FASEB J. 2007;21:1403–1409. - PubMed
-
- Li CM, Park JH, Simonaro CM, He X, Gordon RE, Friedman AH, Ehleiter D, Paris F, Manova K, Hepbildikler S, Fuks Z, Sandhoff K, Kolesnick R, Schuchman EH. Insertional mutagenesis of the mouse acid ceramidase gene leads to early embryonic lethality in homozygotes and progressive lipid storage disease in heterozygotes. Genomics. 2002;79:218–224. - PubMed
-
- Sugita M, Dulaney J, Moser HW. Ceramidase deficiency in Farber’s disease (lipogranulomatosis) Science. 1975;178:1100–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
