Alternative modes of binding of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 to free DNA and nucleosomes
- PMID: 22854955
- PMCID: PMC3463355
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.397067
Alternative modes of binding of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 to free DNA and nucleosomes
Abstract
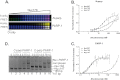
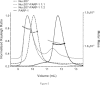
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) is an abundant nuclear protein that binds chromatin and catalyzes the transfer of ADP-ribose groups to itself and to numerous target proteins upon interacting with damaged DNA. The molecular basis for the dual role of PARP-1 as a chromatin architectural protein and a first responder in DNA repair pathways remains unclear. Here, we quantified the interactions of full-length PARP-1 and its N-terminal half with different types of DNA damage and with defined nucleosome substrates. We found that full-length PARP-1 prefers nucleosomes with two linker DNA extensions over any other substrate (including several free DNA models) and that the C-terminal half of PARP-1 is necessary for this selectivity. We also measured the ability of various substrates to activate PARP-1 activity and found that the most important feature for activation is one free DNA end rather than tight interaction with the activating nucleic acid. Our data provide insight into the different modes of interaction of this multidomain protein with nucleosomes and free DNA.
Figures





References
-
- Lord C. J., Ashworth A. (2012) The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature 481, 287–294 - PubMed
-
- Krishnakumar R., Gamble M. J., Frizzell K. M., Berrocal J. G., Kininis M., Kraus W. L. (2008) Reciprocal binding of PARP-1 and histone H1 at promoters specifies transcriptional outcomes. Science 319, 819–821 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

