Human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) is a novel target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human cancer
- PMID: 22854964
- PMCID: PMC3463325
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.368282
Human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) is a novel target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human cancer
Abstract
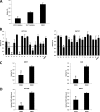
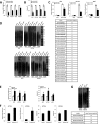
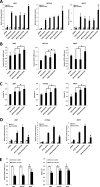
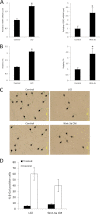
Telomerase activation plays a critical role in human carcinogenesis through the maintenance of telomeres, but the activation mechanism during carcinogenesis remains unclear. The human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) promoter has been shown to promote hTERT gene expression selectively in tumor cells but not in normal cells. Deregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is reported to be associated with human carcinogenesis. However, little is known about whether the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is involved in activating hTERT transcription and inducing telomerase activity (TA). In this study, we report that hTERT is a novel target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Transient activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway either by transfection of a constitutively active form of β-catenin or by LiCl or Wnt-3a conditioned medium treatment induced hTERT mRNA expression and elevated TA in different cell lines. Furthermore, we found that silencing endogenous β-catenin expression by β-catenin gene-specific shRNA effectively decreased hTERT expression, suppressed TA, and accelerated telomere shortening. Of the four members of the lymphoid-enhancing factor (LEF)/T-cell factor (TCF) family, only TCF4 showed more effective stimulation on the hTERT promoter. Ectopic expression of a dominant negative form of TCF4 inhibited hTERT expression in cancer cells. Through promoter mapping, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, we found that hTERT is a direct target of β-catenin·TCF4-mediated transcription and that the TCF4 binding site at the hTERT promoter is critical for β-catenin·TCF4-dependent expression regulation. Given the pivotal role of telomerase in carcinogenesis, these results may offer insight into the regulation of telomerase in human cancer.
Figures



References
-
- Blackburn E. H. (1991) Telomeres. Trends Biochem. Sci. 16, 378–381 - PubMed
-
- Perrem K., Bryan T. M., Englezou A., Hackl T., Moy E. L., Reddel R. R. (1999) Repression of an alternative mechanism for lengthening of telomeres in somatic cell hybrids. Oncogene 18, 3383–3390 - PubMed
-
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. (1989) A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature 337, 331–337 - PubMed
-
- Blasco M. A., Hahn W. C. (2003) Evolving views of telomerase and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 289–294 - PubMed
-
- Kim N. W., Piatyszek M. A., Prowse K. R., Harley C. B., West M. D., Ho P. L., Coviello G. M., Wright W. E., Weinrich S. L., Shay J. W. (1994) Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 266, 2011–2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

