Interaction between isolated transcriptional activation domains of Sp1 revealed by heteronuclear magnetic resonance
- PMID: 22855260
- PMCID: PMC3526990
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2137
Interaction between isolated transcriptional activation domains of Sp1 revealed by heteronuclear magnetic resonance
Abstract
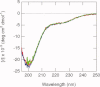
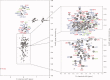
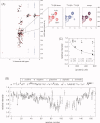
The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 is expressed ubiquitously, and plays a primary role in the regulation of the expression of many genes. Domains A and B located in the N-terminal half of the protein are characterized by glutamine-rich (Q-rich) sequences. These Q-rich domains have been shown to be involved in the interaction between Sp1 and different classes of nuclear proteins, such as TATA-binding protein associated factors. Furthermore, the self-association of Sp1 via Q-rich domains is also important for the regulation of transcriptional activity. It has been considered that an Sp1 molecule bound to a "distal" GC-box synergistically interacts with another Sp1 molecule at a "proximal" binding site. Although the formation of multimers via Q-rich domains seems functionally important for Sp1, little is known about the structural and physicochemical nature of the interaction between Q-rich domains. We analyzed the structural details of isolated glutamine-rich B (QB) domains of Sp1 by circular dichroism (CD), analytical ultracentrifugation, and heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). We found the isolated QB domains to be disordered under all conditions examined. Nevertheless, a detailed analysis of NMR spectra clearly indicated interaction between the domains. In particular, the C-terminal half was responsible for the self-association. Furthermore, analytical ultracentrifugation demonstrated weak but significant interaction between isolated QB domains. The self-association between QB domains would be responsible, at least in part, for the formation of multimers by full-length Sp1 molecules that has been proposed to occur during transcriptional activation.
Copyright © 2012 The Protein Society.
Figures


References
-
- Kavurma MM, Santiago FS, Bonfoco E, Khachigian LM. Sp1 phosphorylation regulates apoptosis via extracellular FasL-Fas engagement. J Biol Chem. 2001;275:4964–4971. - PubMed
-
- Courey AJ, Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988;55:887–898. - PubMed
-
- Kadonaga JT, Carner KR, Masiarz FR, Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987;51:1079–1090. - PubMed
-
- Elrod-Erickson M, Pabo CO. Binding studies with mutants of Zif268. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19281–19285. - PubMed
-
- Wilkins RC, Lis JT. DNA distortion and multimerization: novel functions of the glutamine-rich domain of GAGA factor. J Mol Biol. 1999;285:515–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

