Evaluation of in-house ELISA using Trypanosoma cruzi lysate and recombinant antigens for diagnosis of Chagas disease and discrimination of its clinical forms
- PMID: 22855757
- PMCID: PMC3414563
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.11-0533
Evaluation of in-house ELISA using Trypanosoma cruzi lysate and recombinant antigens for diagnosis of Chagas disease and discrimination of its clinical forms
Abstract
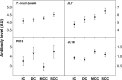
The aim of this work was to investigate the potential usefulness of Trypanosoma cruzi lysate, recombinant protein JL7, and peptides P013, R13, JL18, JL19, and P0β as serological markers for human Chagas disease. We analyzed 228 sera from Brazilian Chagas disease patients classified into four clinical groups and 108 from non-chagasic patients. We defined the diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, and Kappa index measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). As previously described, the highest values of diagnostic parameters were achieved for T. cruzi lysate and JL7; peptide P013 showed high specificity but low sensitivity. The other peptides resulted in lower sensitivity and specificity in our ELISA than T. cruzi lysate and JL7 protein. Antibodies against JL7 protein were mainly detected in sera from patients with severe chagasic cardiomyopathy, compared with those from the indeterminate form, whereas peptides failed to discriminate between the clinical forms of the disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant proteins as promising antigens applied to the immunodiagnosis of Chagas disease: a scoping review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 30;15:1420226. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1420226. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39139374 Free PMC article.
-
The use of peptides for immunodiagnosis of human Chagas disease.Amino Acids. 2024 May 2;56(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03394-6. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 38698213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological diagnosis of Chagas' disease employing a Trypanosoma cruzi recombinant antigen that consists of four different peptides.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Dec;39(12):4390-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4390-4395.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11724850 Free PMC article.
-
Chagas disease-specific antigens: characterization of epitopes in CRA/FRA by synthetic peptide mapping and evaluation by ELISA-peptide assay.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Dec 3;13:568. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-568. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24299278 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of IgM antibodies to Trypanosoma cruzi urinary antigen in sera from patients with acute Chagas' disease.Int J Parasitol. 1998 Apr;28(4):589-94. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(98)00017-4. Int J Parasitol. 1998. PMID: 9602379
Cited by
-
In vitro diagnostic methods of Chagas disease in the clinical laboratory: a scoping review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 30;15:1393992. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1393992. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38746745 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant proteins as promising antigens applied to the immunodiagnosis of Chagas disease: a scoping review.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 30;15:1420226. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1420226. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39139374 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Trypanosoma cruzi infection in naturally infected dogs and cats using serological, parasitological and molecular methods.Acta Trop. 2013 Jun;126(3):211-7. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23499860 Free PMC article.
-
The use of peptides for immunodiagnosis of human Chagas disease.Amino Acids. 2024 May 2;56(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03394-6. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 38698213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Chagas Disease in the Brazilian Amazon: Serological Survey, Clinical Follow-Up, and Associated Risk Factors.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025 Mar 25;112(6):1220-1228. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.24-0549. Print 2025 Jun 4. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025. PMID: 40132217
References
-
- PAHO-WHO . 2006. Estimación cuantitativa de la enfermedad de Chagas en las Américas. OPS/HDM/CD/425-06.
-
- World Health Organization . Control of Chagas disease: Second Report of the WHO Expert Committee. Geneva: WHO; 2002. WHO Technical report series 905.
-
- Muniz J, Freitas G. Contribuição para o diagnóstico da doença de Chagas pelas reações de imunidade. II - Isolamento de polissacarídeos de Schizotrypanum cruzi e de outros tripanosomídeos, seu comportamento nas reações de precipitação, de fixação do complemento e de hipersensibilidade. Os “Tests” de floculação (sublimado e formol-gel) Rev Bras Biol. 1944;4:421–438.
-
- Cerisola JA, Rosenbaum MB. Complement-fixation reaction in the diagnosis of Chagas' disease. Prensa Med Argent. 1958;45:1454–1463. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez M, Cerisola JA, Rohweder RW. Test de inmunofluorescencia para el diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Chagas. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1968;23:4–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

