Spatial and functional relationships among Pol V-associated loci, Pol IV-dependent siRNAs, and cytosine methylation in the Arabidopsis epigenome
- PMID: 22855789
- PMCID: PMC3426761
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.197772.112
Spatial and functional relationships among Pol V-associated loci, Pol IV-dependent siRNAs, and cytosine methylation in the Arabidopsis epigenome
Abstract
Multisubunit RNA polymerases IV and V (Pols IV and V) mediate RNA-directed DNA methylation and transcriptional silencing of retrotransposons and heterochromatic repeats in plants. We identified genomic sites of Pol V occupancy in parallel with siRNA deep sequencing and methylcytosine mapping, comparing wild-type plants with mutants defective for Pol IV, Pol V, or both Pols IV and V. Approximately 60% of Pol V-associated regions encompass regions of 24-nucleotide (nt) siRNA complementarity and cytosine methylation, consistent with cytosine methylation being guided by base-pairing of Pol IV-dependent siRNAs with Pol V transcripts. However, 27% of Pol V peaks do not overlap sites of 24-nt siRNA biogenesis or cytosine methylation, indicating that Pol V alone does not specify sites of cytosine methylation. Surprisingly, the number of methylated CHH motifs, a hallmark of RNA-directed de novo methylation, is similar in wild-type plants and Pol IV or Pol V mutants. In the mutants, methylation is lost at 50%-60% of the CHH sites that are methylated in the wild type but is gained at new CHH positions, primarily in pericentromeric regions. These results indicate that Pol IV and Pol V are not required for cytosine methyltransferase activity but shape the epigenome by guiding CHH methylation to specific genomic sites.
Figures

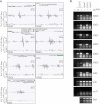
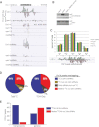
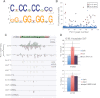
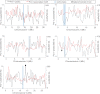

Comment in
-
Seeing the forest for the trees: a wide perspective on RNA-directed DNA methylation.Genes Dev. 2012 Aug 15;26(16):1769-73. doi: 10.1101/gad.200410.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22895250 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomics: dissecting the roles of Pol V.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Oct;13(10):673. doi: 10.1038/nrg3328. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22929988 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cao X, Jacobsen SE 2002. Role of the Arabidopsis DRM methyltransferases in de novo DNA methylation and gene silencing. Curr Biol 12: 1138–1144 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
