Condensins: universal organizers of chromosomes with diverse functions
- PMID: 22855829
- PMCID: PMC3418584
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.194746.112
Condensins: universal organizers of chromosomes with diverse functions
Abstract
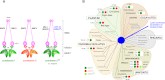
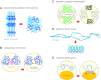
Condensins are multisubunit protein complexes that play a fundamental role in the structural and functional organization of chromosomes in the three domains of life. Most eukaryotic species have two different types of condensin complexes, known as condensins I and II, that fulfill nonoverlapping functions and are subjected to differential regulation during mitosis and meiosis. Recent studies revealed that the two complexes contribute to a wide variety of interphase chromosome functions, such as gene regulation, recombination, and repair. Also emerging are their cell type- and tissue-specific functions and relevance to human disease. Biochemical and structural analyses of eukaryotic and bacterial condensins steadily uncover the mechanisms of action of this class of highly sophisticated molecular machines. Future studies on condensins will not only enhance our understanding of chromosome architecture and dynamics, but also help address a previously underappreciated yet profound set of questions in chromosome biology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Condensin action and compaction.Curr Genet. 2019 Apr;65(2):407-415. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0899-4. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30361853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Condensin I and II behaviour in interphase nuclei and cells undergoing premature chromosome condensation.Chromosome Res. 2016 May;24(2):243-69. doi: 10.1007/s10577-016-9519-7. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Chromosome Res. 2016. PMID: 27008552
-
Condensin Regulation of Genome Architecture.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Jul;232(7):1617-1625. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25702. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27888504 Review.
-
Condensin-Based Chromosome Organization from Bacteria to Vertebrates.Cell. 2016 Feb 25;164(5):847-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.033. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26919425 Review.
-
Condensins I and II are essential for construction of bivalent chromosomes in mouse oocytes.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Sep;22(18):3465-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0423. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21795393 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Condensin-mediated chromosome organization and gene regulation.Front Genet. 2015 Jan 13;5:473. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00473. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25628648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome Compaction by Active Loop Extrusion.Biophys J. 2016 May 24;110(10):2162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.02.041. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27224481 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in NCAPG2 Cause a Severe Neurodevelopmental Syndrome that Expands the Phenotypic Spectrum of Condensinopathies.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Jan 3;104(1):94-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.11.017. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30609410 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear architecture and the structural basis of mitotic memory.Chromosome Res. 2023 Feb 2;31(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s10577-023-09714-y. Chromosome Res. 2023. PMID: 36725757 Review.
-
Function and Evolution of the Loop Extrusion Machinery in Animals.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 6;24(5):5017. doi: 10.3390/ijms24055017. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902449 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akai Y, Kurokawa Y, Nakazawa N, Tonami-Murakami Y, Suzuki Y, Yoshimura S-H, Iwasaki H, Shiroiwa Y, Nakamura T, Shibata E, et al. 2011. Opposing role of condensin hinge against replication protein A in mitosis and interphase through promoting DNA annealing. Open Biol 1: 110023 doi: 10.1098/rsob.110023 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alderton GK, Galbiati L, Griffith E, Surinya KH, Neitzel H, Jackson AP, Jeggo PA, O'Driscoll M 2006. Regulation of mitotic entry by microcephalin and its overlap with ATP signalling. Nat Cell Biol 8: 725–733 - PubMed
-
- Aono N, Sutani T, Tomonaga T, Mochida S, Yanagida M 2002. Cnd2 has dual roles in mitotic condensation and interphase. Nature 417: 197–202 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
