Autoregulation of TDP-43 mRNA levels involves interplay between transcription, splicing, and alternative polyA site selection
- PMID: 22855830
- PMCID: PMC3418585
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.194829.112
Autoregulation of TDP-43 mRNA levels involves interplay between transcription, splicing, and alternative polyA site selection
Abstract
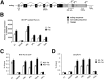
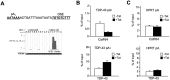
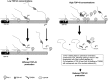
TDP-43 is a critical RNA-binding factor associated with pre-mRNA splicing in mammals. Its expression is tightly autoregulated, with loss of this regulation implicated in human neuropathology. We demonstrate that TDP-43 overexpression in humans and mice activates a 3' untranslated region (UTR) intron, resulting in excision of the proximal polyA site (PAS) pA(1). This activates a cryptic PAS that prevents TDP-43 expression through a nuclear retention mechanism. Superimposed on this process, overexpression of TDP-43 blocks recognition of pA(1) by competing with CstF-64 for PAS binding. Overall, we uncover complex interplay between transcription, splicing, and 3' end processing to effect autoregulation of TDP-43.
Figures


References
-
- Ayala YM, Zago P, D'Ambrogio A, Xu YF, Petrucelli L, Buratti E, Baralle FE 2008. Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43. J Cell Sci 121: 3778–3785 - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE 2001. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem 276: 36337–36343 - PubMed
-
- Buratti E, Baralle FE 2011. TDP-43: New aspects of autoregulation mechanisms in RNA binding proteins and their connection with human disease. FEBS J 278: 3530–3538 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
