Unraveling the KNOTTED1 regulatory network in maize meristems
- PMID: 22855831
- PMCID: PMC3418586
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.193433.112
Unraveling the KNOTTED1 regulatory network in maize meristems
Abstract
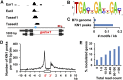
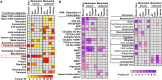
KNOTTED1 (KN1)-like homeobox (KNOX) transcription factors function in plant meristems, self-renewing structures consisting of stem cells and their immediate daughters. We defined the KN1 cistrome in maize inflorescences and found that KN1 binds to several thousand loci, including 643 genes that are modulated in one or multiple tissues. These KN1 direct targets are strongly enriched for transcription factors (including other homeobox genes) and genes participating in hormonal pathways, most significantly auxin, demonstrating that KN1 plays a key role in orchestrating the upper levels of a hierarchical gene regulatory network that impacts plant meristem identity and function.
Figures


References
-
- Biggin MD 2011. Animal transcription networks as highly connected, quantitative continua. Dev Cell 21: 611–626 - PubMed
-
- Chapman EJ, Estelle M 2009. Mechanism of auxin-regulated gene expression in plants. Annu Rev Genet 43: 265–285 - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Banerjee AK, Hannapel DJ 2004. The tandem complex of BEL and KNOX partners is required for transcriptional repression of ga20ox1. Plant J 38: 276–284 - PubMed
-
- Doebley J, Stec A, Hubbard L 1997. The evolution of apical dominance in maize. Nature 386: 485–488 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
