Resveratrol inhibits inflammation induced by heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 22857612
- PMCID: PMC3429294
- DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2194
Resveratrol inhibits inflammation induced by heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
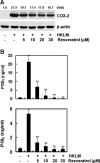
Resveratrol is a polyphenolic compound in red wine that has antioxidant and cardioprotective effects in animal models. Listeria monocytogenes is a pathogen that mainly affects immunocompromised individuals and is initially detected at the cell surface or in phagosomes by toll-like receptor 2. Many antioxidants also exert anti-inflammatory activities; therefore, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory properties of resveratrol by studying the various inflammatory responses induced by heat-killed L. monocytogenes (HKLM). Resveratrol strongly blocked HKLM-induced NADPH oxidase-1 mRNA and reactive oxygen species production by macrophages. Resveratrol also suppressed monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression, cyclooxygenase-2 expression, prostaglandin production, inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase expression, and NO production induced by HKLM. We investigated the signaling pathway involved in the resveratrol effect. HKLM stimulated glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation. The involvement of GSK3β and ERK1/2 was tested using inhibitors. While the GSK3β inhibitor LiCl potentiated the effect of HKLM, the MEK inhibitor U0126 blocked these responses. Additionally, pretreatment with resveratrol blocked phosphorylation of both kinases induced by HKLM. These results suggest that HKLM is strong inducer of inflammatory mediators, and that the inhibitory effect of resveratrol may be mediated by the GSK3β and ERK1/2 pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced MAPKs activation via activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044107. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952890 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol inhibits foam cell formation via NADPH oxidase 1- mediated reactive oxygen species and monocyte chemotactic protein-1.Exp Mol Med. 2009 Mar 31;41(3):171-9. doi: 10.3858/emm.2009.41.3.020. Exp Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19293636 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory responses via the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in cultured LPS-stimulated microglial cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032195. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363816 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of resveratrol in in vitro and in vivo experimental cerebral stroke models.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Aug 21;4(8):1151-62. doi: 10.1021/cn400094w. Epub 2013 Jun 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23758534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol (RV): A pharmacological review and call for further research.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112164. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112164. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34649335 Review.
Cited by
-
Finding Ponce de Leon's Pill: Challenges in Screening for Anti-Aging Molecules.F1000Res. 2016 Mar 29;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-406. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7821.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27081480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannan-BAM, TLR ligands, and anti-CD40 immunotherapy in established murine pancreatic adenocarcinoma: understanding therapeutic potentials and limitations.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Nov;70(11):3303-3312. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02920-9. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33855601 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation via the Hippo Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Oct 13;2021:3399357. doi: 10.1155/2021/3399357. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34690551 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of resveratrol against ethanol-induced oxidative stress through induction of superoxide dismutase in vivo and in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2016 Apr;11(4):1231-1238. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3077. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Exp Ther Med. 2016. PMID: 27073428 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule SIRT1 activators for the treatment of aging and age-related diseases.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Mar;35(3):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.12.004. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24439680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pervaiz S. Resveratrol: from grapevines to mammalian biology. FASEB J. 2003;17:1975–1985. - PubMed
-
- Zang M. Xu S. Maitland-Toolan KA. Zuccollo A. Hou X. Jiang B. Wierzbicki M. Verbeuren TJ. Cohen RA. Polyphenols stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase, lower lipids, and inhibit accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic LDL receptor-deficient mice. Diabetes. 2006;55:2180–2191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

