Progranulin: a proteolytically processed protein at the crossroads of inflammation and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 22859297
- PMCID: PMC3463300
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.399170
Progranulin: a proteolytically processed protein at the crossroads of inflammation and neurodegeneration
Abstract
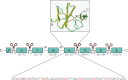
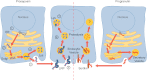
GRN mutations cause frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43-positive inclusions. The mechanism of pathogenesis is haploinsufficiency. Recently, homozygous GRN mutations were detected in two patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, a lysosomal storage disease. It is unknown whether the pathogenesis of these two conditions is related. Progranulin is cleaved into smaller peptides called granulins. Progranulin and granulins are attributed with roles in cancer, inflammation, and neuronal physiology. Cell surface receptors for progranulin, but not granulin peptides, have been reported. Revealing the cell surface receptors and the intracellular functions of granulins and progranulin is crucial for understanding their contributions to neurodegeneration.
Figures
References
-
- Daniel R., He Z., Carmichael K. P., Halper J., Bateman A. (2000) Cellular localization of gene expression for progranulin. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 48, 999–1009 - PubMed
-
- Daniel R., Daniels E., He Z., Bateman A. (2003) Progranulin (acrogranin/PC cell-derived growth factor/granulin-epithelin precursor) is expressed in the placenta, epidermis, microvasculature, and brain during murine development. Dev. Dyn. 227, 593–599 - PubMed
-
- Mackenzie I. R., Baker M., Pickering-Brown S., Hsiung G. Y., Lindholm C., Dwosh E., Gass J., Cannon A., Rademakers R., Hutton M., Feldman H. H. (2006) The neuropathology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration caused by mutations in the progranulin gene. Brain 129, 3081–3090 - PubMed
-
- Matsubara T., Mita A., Minami K., Hosooka T., Kitazawa S., Takahashi K., Tamori Y., Yokoi N., Watanabe M., Matsuo E., Nishimura O., Seino S. (2012) PGRN is a key adipokine mediating high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity through IL-6 in adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 15, 38–50 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

