Dysregulated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system contributes to pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 22859525
- PMCID: PMC5104838
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201203-0411OC
Dysregulated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system contributes to pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (iPAH) often have a low cardiac output. To compensate, neurohormonal systems such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) and the sympathetic nervous system are up-regulated, but this may have long-term negative effects on the progression of iPAH.
Objectives: Assess systemic and pulmonary RAAS activity in patients with iPAH and determine the efficacy of chronic RAAS inhibition in experimental PAH.
Methods: We collected 79 blood samples from 58 patients with iPAH in the VU University Medical Center Amsterdam (between 2004 and 2010) to determine systemic RAAS activity.
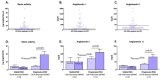
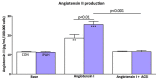
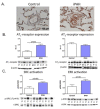
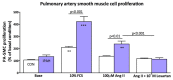
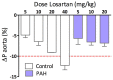
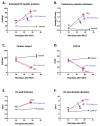
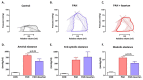
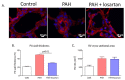
Measurements and main results: We observed increased levels of renin, angiotensin (Ang)I, and AngII, which were associated with disease progression (P < 0.05) and mortality (P < 0.05). To determine pulmonary RAAS activity, lung specimens were obtained from patients with iPAH (during lung transplantation, n = 13) and control subjects (during lobectomy or pneumonectomy for cancer, n = 14). Local RAAS activity in pulmonary arteries of patients with iPAH was increased, demonstrated by elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in pulmonary endothelial cells and increased AngII type 1 (AT(1)) receptor expression and signaling. In addition, local RAAS up-regulation was associated with increased pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation via enhanced AT(1) receptor signaling in patients with iPAH compared with control subjects. Finally, to determine the therapeutic potential of RAAS activity, we assessed the chronic effects of an AT(1) receptor antagonist (losartan) in the monocrotaline PAH rat model (60 mg/kg). Losartan delayed disease progression, decreased right ventricular afterload and pulmonary vascular remodeling, and restored right ventricular-arterial coupling in rats with PAH.
Conclusions: Systemic and pulmonary RAAS activities are increased in patients with iPAH and are associated with increased pulmonary vascular remodeling. Chronic inhibition of RAAS by losartan is beneficial in experimental PAH.
Figures
Comment in
-
TrACEing angiotensin II type 1 to right ventricular hypertrophy: are the "sartans" a viable course to treating pulmonary arterial hypertension?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Oct 15;186(8):705-7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201208-1480ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 23071186 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The renin-angiotensin system in pulmonary hypertension.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 May 15;187(10):1138-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201210-1872LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23675718 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply: The renin-angiotensin system in pulmonary hypertension.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 May 15;187(10):1139-40. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201301-0109LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013. PMID: 23675720 No abstract available.
References
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, Bertocchi M, Habib G, Gressin V, Yaici A, Weitzenblum E, Cordier JF, Chabot F, Dromer C, Pison C, Reynaud-Gaubert M, Haloun A, Laurent M, Hachulla E, Cottin V, Degano B, Jais X, Montani D, Souza R, Simonneau G. Survival in patients with idiopathic, familial, and anorexigen-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Circulation. 2010;122:156–163. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorn EJ, Bristow MR. Medical therapy can improve the biological properties of the chronically failing heart. A new era in the treatment of heart failure. Circulation. 1996;94:2285–2296. - PubMed
-
- Ciarka A, Doan V, Velez-Roa S, Naeije R, van de Borne P. Prognostic significance of sympathetic nervous system activation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;181:1269–1275. - PubMed
-
- de Man FS, Handoko ML, van Ballegoij JJ, Schalij I, Bogaards SJ, Postmus PE, van dV, Westerhof N, Paulus WJ, Vonk-Noordegraaf A. Bisoprolol delays progression towards right heart failure in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Circ Heart Fail. 2012;5:97–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

