Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: a subgroup analysis evaluating Japanese patients in the RADIANT-3 trial
- PMID: 22859827
- PMCID: PMC3448379
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hys123
Everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: a subgroup analysis evaluating Japanese patients in the RADIANT-3 trial
Abstract
Objective: Everolimus, an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin, has recently demonstrated efficacy and safety in a Phase III, double-blind, randomized trial (RADIANT-3) in 410 patients with low- or intermediate-grade advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Everolimus 10 mg/day provided a 2.4-fold improvement compared with placebo in progression-free survival, representing a 65% risk reduction for progression. The purpose of this analysis was to investigate the efficacy and safety of everolimus in the Japanese subgroup enrolled in the RADIANT-3 study.
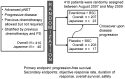
Methods: Subgroup analysis of the Japanese patients was performed comparing efficacy and safety between everolimus 10 mg/day orally (n = 23) and matching placebo (n = 17). The primary endpoint was progression-free survival. Safety was evaluated on the basis of the incidence of adverse drug reactions.
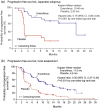
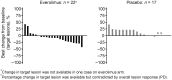
Results: Progression-free survival was significantly prolonged with everolimus compared with placebo. The median progression-free survival was 19.45 months (95% confidence interval, 8.31-not available) with everolimus vs 2.83 months (95% confidence interval, 2.46-8.34) with placebo, resulting in an 81% risk reduction in progression (hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.08-0.48; P< 0.001). Adverse drug reactions occurred in all 23 (100%) Japanese patients receiving everolimus and in 13 (77%) patients receiving placebo; most were grade 1/2 in severity. The most common adverse drug reactions in the everolimus group were rash (n = 20; 87%), stomatitis (n = 17; 74%), infections (n = 15; 65%), nail disorders (n = 12; 52%), epistaxis (n = 10; 44%) and pneumonitis (n = 10; 44%).
Conclusions: These results support the use of everolimus as a valuable treatment option for Japanese patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours.
Figures
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, et al. One hundred years after ‘carcinoid’: epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–72. - PubMed
-
- Ito T, Sasano H, Tanaka M, et al. Epidemiological study of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:234–43. - PubMed
-
- Capurso G, Fazio N, Festa S, Panzuto F, de Braud F, Delle Fave G. Molecular target therapy for gastroenteropancreatic endocrine tumours: biological rationale and clinical perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;72:110–24. - PubMed
-
- Basu B, Sirohi B, Corrie P. Systemic therapy for neuroendocrine tumours of gastroenteropancreatic origin. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17:R75–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

