Absence of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (Cftr) from myeloid-derived cells slows resolution of inflammation and infection
- PMID: 22859830
- PMCID: PMC3476241
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0412188
Absence of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (Cftr) from myeloid-derived cells slows resolution of inflammation and infection
Abstract
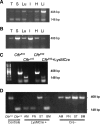
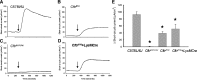
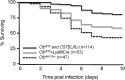
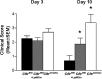
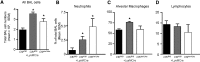
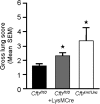
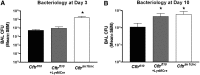
The absence or reduction of CFTR function causes CF and results in a pulmonary milieu characterized by bacterial colonization and unresolved inflammation. The ineffectiveness at controlling infection by species such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa suggests defects in innate immunity. Macrophages, neutrophils, and DCs have all been shown to express CFTR mRNA but at low levels, raising the question of whether CFTR has a functional role in these cells. Bone marrow transplants between CF and non-CF mice suggest that these cells are inherently different; we confirm this observation using conditional inactivation of Cftr in myeloid-derived cells. Mice lacking Cftr in myeloid cells overtly appear indistinguishable from non-CF mice until challenged with bacteria instilled into the lungs and airways, at which point, they display survival and inflammatory profiles intermediate in severity as compared with CF mice. These studies demonstrate that Cftr is involved directly in myeloid cell function and imply that these cells contribute to the pathophysiological phenotype of the CF lung.
Figures


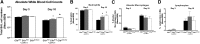
References
-
- Mueller C., Braag S. A., Keeler A., Hodges C., Drumm M., Flotte T. R. (2011) Lack of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in CD3+ lymphocytes leads to aberrant cytokine secretion and hyperinflammatory adaptive immune responses. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 44, 922–929 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babaev V. R., Yancey P. G., Ryzhov S. V., Kon V., Breyer M. D., Magnuson M. A., Fazio S., Linton M. F. (2005) Conditional knockout of macrophage PPARγ increases atherosclerosis in C57BL/6 and low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25, 1647–1653 - PubMed
-
- Thomassen M. J., Barna B. P., Malur A. G., Bonfield T. L., Farver C. F., Malur A., Dalrymple H., Kavuru M. S., Febbraio M. (2007) ABCG1 is deficient in alveolar macrophages of GM-CSF knockout mice and patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J. Lipid Res. 48, 2762–2768 - PubMed
-
- Bonfield T., Raychaudhuri L., Malur B., Abraham A., Trapnell S. B. C., Kavuru M. S., Thomassen M. J. (2003) PU. 1 regulation of human alveolar macrophage differentiation requires granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 285, L1132–L1136 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

