Aquaporin 2 promotes cell migration and epithelial morphogenesis
- PMID: 22859853
- PMCID: PMC3431417
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012010079
Aquaporin 2 promotes cell migration and epithelial morphogenesis
Abstract
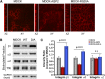
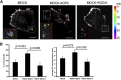
The aquaporin 2 (AQP2) water channel, expressed in kidney collecting ducts, contributes critically to water homeostasis in mammals. Animals lacking or having significantly reduced levels of AQP2, however, have not only urinary concentrating abnormalities but also renal tubular defects that lead to neonatal mortality from renal failure. Here, we show that AQP2 is not only a water channel but also an integrin-binding membrane protein that promotes cell migration and epithelial morphogenesis. AQP2 expression modulates the trafficking and internalization of integrin β1, facilitating its turnover at focal adhesions. In vitro, disturbing the interaction between AQP2 and integrin β1 by mutating the RGD motif led to reduced endocytosis, retention of integrin β1 at the cell surface, and defective cell migration and tubulogenesis. Similarly, in vivo, AQP2-null mice exhibited significant retention of integrin β1 at the basolateral membrane and had tubular abnormalities. In summary, these data suggest that the water channel AQP2 interacts with integrins to promote renal epithelial cell migration, contributing to the structural and functional integrity of the mammalian kidney.
Figures
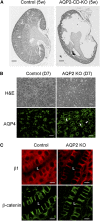
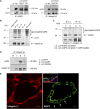
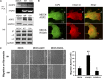
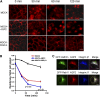
Comment in
-
Aquaporin 2: not just for moving water.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Sep;23(9):1443-4. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012060613. Epub 2012 Jul 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22797179 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brown D: The ins and outs of aquaporin-2 trafficking. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284: F893–F901, 2003 - PubMed
-
- van Balkom BW, Graat MP, van Raak M, Hofman E, van der Sluijs P, Deen PM: Role of cytoplasmic termini in sorting and shuttling of the aquaporin-2 water channel. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286: C372–C379, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Sun TX, Van Hoek A, Huang Y, Bouley R, McLaughlin M, Brown D: Aquaporin-2 localization in clathrin-coated pits: Inhibition of endocytosis by dominant-negative dynamin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282: F998–F1011, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Lu H, Sun TX, Bouley R, Blackburn K, McLaughlin M, Brown D: Inhibition of endocytosis causes phosphorylation (S256)-independent plasma membrane accumulation of AQP2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286: F233–F243, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

