Sofnolime with different water content causes different effects in two sevoflurane inhalational induction techniques with respect to the output of compound-A
- PMID: 22859903
- PMCID: PMC3410362
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.4436
Sofnolime with different water content causes different effects in two sevoflurane inhalational induction techniques with respect to the output of compound-A
Abstract
Objective: During sevoflurane anesthesia with Sofnolime for CO(2) absorption, the factors affecting the production of compound A (a chemical is nepherotoxic) are still not clear. This study is designed to investigate the effects of different fresh gas flow during induction, the vital capacity induction (VCI) vs. the tidal volume breath induction (TBI) on the compound-A production with a fresh Sofnolime or a dehydrated Sofnolime using a simulated lung model.
Method: The experiments were randomly divided into four groups: group one, VCIf, vital capacity fresh gas inflow with fresh Sofnolime; group two, TBIf, tidal volume breath fresh gas inflow with fresh Sofnolime; group three, VCId, vital capacity fresh gas inflow with dehydrated Sofnolime, and group four, TBId, tidal volume breath fresh gas inflow with dehydrated Sofnolime. The inspired sevoflurane was maintained at 8%, the concentrations of compound-A were assayed using Gas-spectrum technique, and Sofnolime temperatures were monitored at 1-min intervals throughout the experiment.
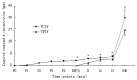
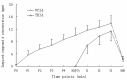
Results: The mean and maximum concentrations of compound A were significantly higher in the vital capacity group than the tidal volume breath group (P<0.01). At the beginning of anesthesia maintenance, the compound-A concentration in group VCIf was 36.28±6.13 ppm, which was significantly higher than the 27.32±4.21 ppm observed in group TBIf (P<0.01). However, these values decreased to approximately 2 ppm in the dehydrated Sofnolime groups. Sofnolime temperatures increased rapidly in the dehydrated Sofnolime groups but slowly in the fresh Sofnolime groups.
Conclusion: With fresh Sofnolime, vital capacity induction increased compound-A production in the circuit system compared with tidal volume breath induction. However, with dehydrated Sofnolime, the effects of the two inhalation induction techniques on compound-A output were not significantly different.
Keywords: Sofnolime; anesthesia; compound-A; inhalation; model lung.; sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Fritsch N, Nouette-Gaulain K, Bordes M. et al. Target-controlled inhalation induction with sevoflurane in children: a prospective pilot study. Paediat Anaesth. 2009;19:126–32. - PubMed
-
- Lesage S, Drolet P, Donati F. et al. Low-dose fentanyl-midazolam combination improves sevoflurane induction in adults. Can J Anaesth. 2009;56:733–9. - PubMed
-
- Lin TC, Lu CC, Kuo CK. et al. Single vital-capacity and successive tidal-volume breathing of sevoflurane in induction of anesthesia for tracheal intubation in gynecologic patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2008;46:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Xue FS, Liao X, Li CW. et al. Clinical experience of airway management and tracheal intubation under general anesthesia in patients with scar contracture of the neck. Chin Med J. 2008;121:989–97. - PubMed
-
- Behne M, Wilke HJ, Harder S. Clinical pharmacokinetics of sevoflurane. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;36:13–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

