Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 22859929
- PMCID: PMC3403247
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X11436240
Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Imaging is an integral part of the management of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis. Characteristic radiographic and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings are key in the diagnosis. Radiography and MRI are also useful in monitoring the disease. Radiography is the conventional, albeit quite insensitive, gold standard method for assessment of structural damage in spine and sacroiliac joints, whereas MRI has gained a decisive role in monitoring disease activity in clinical trials and practice. MRI may also, if ongoing research demonstrates a sufficient reliability and sensitivity to change, become a new standard method for assessment of structural damage. Ultrasonography allows visualization of peripheral arthritis and enthesitis, but has no role in the assessment of axial manifestations. Computed tomography is a sensitive method for assessment of structural changes in the spine and sacroiliac joints, but its clinical utility is limited due to its use of ionizing radiation and lack of ability to assess the soft tissues. It is exciting that with continued dedicated research and the rapid technical development it is likely that even larger improvements in the use of imaging may occur in the decade to come, for the benefit of our patients.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; computed tomography; imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; radiography; spondyloarthritis; ultrasonography; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
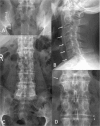
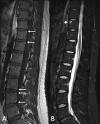
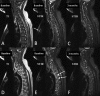
Figures


References
-
- Baraliakos X., Hermann K.G., Landewe R., Listing J., Golder W., Brandt J., et al. (2005) Assessment of acute spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis by magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison between contrast enhanced T1 and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. Ann Rheum Dis 64: 1141–1144 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett A.N., McGonagle D., O’Connor P., Hensor E.M., Sivera F., Coates L.C., et al. (2008) Severity of baseline magnetic resonance imaging-evident sacroiliitis and HLA-B27 status in early inflammatory back pain predict radiographically evident ankylosing spondylitis at eight years. Arthritis Rheum 58: 3413–3418 - PubMed
-
- Berens D.L. (1971) Roentgen features of ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 74: 20–33 - PubMed
-
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Listing J., et al. (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum 48: 1126–1136 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

