Biomarkers of good EULAR response to the B cell depletion therapy in all seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients: clues for the pathogenesis
- PMID: 22859946
- PMCID: PMC3408482
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040362
Biomarkers of good EULAR response to the B cell depletion therapy in all seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients: clues for the pathogenesis
Abstract
Objective: To find out whether a high number of auto-antibodies can increase the probability of a "good-EULAR response" and to identify the possible biomarkers of response in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients undergoing the B cell depletion therapy (BCDT).
Patients and methods: One hundred and thirty-eight patients with long standing RA (LSRA), 75% non or poorly responsive to one or more TNFα blockers, all seropositive for at least one autoantibody (AAB) (RF-IgM, RF-IgA, RF-IgG, anti-MCV, ACPA-IgG, ACPA-IgA, ACPA-IgM) received one full course of BCDT. The major outcomes (moderate or good-EULAR response) were assessed after 6 months of therapy. The IL6 and BAFF levels were also determined.
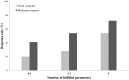
Results: At a 6-month follow-up, 33 (23.9%) of the RA patients achieved a good EULAR response. Having up to 5-AABs positivity increased the chances for treatment response. After a logistic regression analysis, however, only 4 baseline factors arose as associated with a good-EULAR response: no steroid therapy (OR = 6.25), a lymphocyte count <1875/uL (OR = 10.74), a RF-IgG level >52.1 IU/ml (OR = 8.37) and BAFF levels <1011 pg/ml (OR = 7.38). When all the AABs, except for RF-IgM and ACPA-IgG, were left in the analysis, the two final predictors were no-steroid therapy and low lymphocyte count.
Discussion: The number of AABs increased the chances of being a "good-EULAR" responder. The only predictors, however, at the baseline of a good response in this seropositive cohort of RA patients were 2 simple variables--no steroids and lymphocyte count--and two laboratory assays--IgG-RF and BAFF.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Firestein GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423: 356–361. - PubMed
-
- Silverman GJ (2006) Therapeutic B cell depletion and regeneration in rheumatoid arthritis: emerging patterns and paradigms. Arthritis Rheum 54: 2356–67. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill SK, Glant TT, Finnegan A (2007) The role of B cells in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci 12: 1722–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

