Side-by-side comparison of gene-based smallpox vaccine with MVA in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 22860117
- PMCID: PMC3409187
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042353
Side-by-side comparison of gene-based smallpox vaccine with MVA in nonhuman primates
Abstract
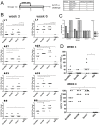
Orthopoxviruses remain a threat as biological weapons and zoonoses. The licensed live-virus vaccine is associated with serious health risks, making its general usage unacceptable. Attenuated vaccines are being developed as alternatives, the most advanced of which is modified-vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA). We previously developed a gene-based vaccine, termed 4pox, which targets four orthopoxvirus antigens, A33, B5, A27 and L1. This vaccine protects mice and non-human primates from lethal orthopoxvirus disease. Here, we investigated the capacity of the molecular adjuvants GM-CSF and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) to enhance the efficacy of the 4pox gene-based vaccine. Both adjuvants significantly increased protective antibody responses in mice. We directly compared the 4pox plus LT vaccine against MVA in a monkeypox virus (MPXV) nonhuman primate (NHP) challenge model. NHPs were vaccinated twice with MVA by intramuscular injection or the 4pox/LT vaccine delivered using a disposable gene gun device. As a positive control, one NHP was vaccinated with ACAM2000. NHPs vaccinated with each vaccine developed anti-orthopoxvirus antibody responses, including those against the 4pox antigens. After MPXV intravenous challenge, all control NHPs developed severe disease, while the ACAM2000 vaccinated animal was well protected. All NHPs vaccinated with MVA were protected from lethality, but three of five developed severe disease and all animals shed virus. All five NHPs vaccinated with 4pox/LT survived and only one developed severe disease. None of the 4pox/LT-vaccinated animals shed virus. Our findings show, for the first time, that a subunit orthopoxvirus vaccine delivered by the same schedule can provide a degree of protection at least as high as that of MVA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Nucleic Acid-Based Orthopoxvirus Vaccine Targeting the Vaccinia Virus L1, A27, B5, and A33 Proteins Protects Rabbits against Lethal Rabbitpox Virus Aerosol Challenge.J Virol. 2022 Feb 9;96(3):e0150421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01504-21. Epub 2021 Dec 1. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34851148 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the orthopoxvirus type I interferon-binding molecule as a vaccine target in the vaccinia virus intranasal murine challenge model.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Nov;17(11):1656-65. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00235-10. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20844086 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular smallpox vaccine delivered by alphavirus replicons elicits protective immunity in mice and non-human primates.Vaccine. 2009 Dec 11;28(2):494-511. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.09.133. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19833247 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical development of Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara vaccines.Vaccine. 2013 Sep 6;31(39):4241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23523410 Review.
-
Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara: History, Value in Basic Research, and Current Perspectives for Vaccine Development.Adv Virus Res. 2017;97:187-243. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Adv Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 28057259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IMVAMUNE® and ACAM2000® Provide Different Protection against Disease When Administered Postexposure in an Intranasal Monkeypox Challenge Prairie Dog Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jul 20;8(3):396. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030396. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32698399 Free PMC article.
-
TLR3 and TLR9 agonists improve postexposure vaccination efficacy of live smallpox vaccines.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 28;9(10):e110545. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110545. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25350003 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid nanoparticle delivery of unmodified mRNAs encoding multiple monoclonal antibodies targeting poxviruses in rabbits.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 May 10;28:847-858. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.05.025. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35664703 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Virulence in Cynomolgus Macaques Using a Virus Preparation Enriched for the Extracellular Form of Monkeypox Virus.Viruses. 2022 Sep 9;14(9):1993. doi: 10.3390/v14091993. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146799 Free PMC article.
-
Poxvirus structural biology for application to vaccine design.Trends Immunol. 2025 Jun;46(6):455-470. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2025.04.002. Epub 2025 May 7. Trends Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40340168 Review.
References
-
- No Smallpox. World Health Organization: Weekly Epidemiological Record 54: 329.
-
- Bhanuprakash V, Venkatesan G, Balamurugan V, Hosamani M, Yogisharadhya R, et al. (2010) Zoonotic Infections of Buffalopox in India. Zoonoses Public Health 57: 149–155. - PubMed
-
- Glatz M, Richter S, Ginter-Hanselmayer G, Aberer W, Mullegger RR (2010) Human cowpox in a veterinary student. Lancet Infect Dis 10: 288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

