Adenosine A(2A) Receptor Antagonists and Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 22860156
- PMCID: PMC3369712
- DOI: 10.1021/cn2000537
Adenosine A(2A) Receptor Antagonists and Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
This Review summarizes and updates the work on adenosine A(2A) receptor antagonists for Parkinson's disease from 2006 to the present. There have been numerous publications, patent applications, and press releases within this time frame that highlight new medicinal chemistry approaches to this attractive and promising target to treat Parkinson's disease. The Review is broken down by scaffold type and will discuss the efforts to optimize particular scaffolds for activity, pharmacokinetics, and other drug discovery parameters. The majority of approaches focus on preparing selective A(2A) antagonists, but a few approaches to dual A(2A)/A(1) antagonists will also be highlighted. The in vivo profiles of compounds will be highlighted and discussed to compare activities across different chemical series. A clinical report and update will be given on compounds that have entered clinical trials.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; A1 receptor antagonist; A2A receptor antagonist; Adenosine; MPTP; Parkinson’s disease; catalepsy.
Figures
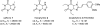
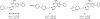
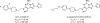
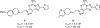
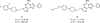
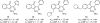
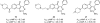
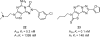
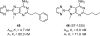
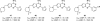
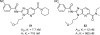
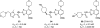
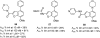
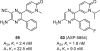
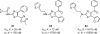
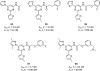
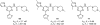
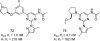
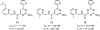
References
-
- Lozano A. M.; Lang A. E.; Hutchison W. D.; Dostrovsky J. O. (1998) New developments in understanding the etiology of Parkinson’s disease and in its treatment. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 8, 783–790. - PubMed
-
- Fink J. S.; Weaver D. R.; Rivkees S. A.; Peterfreund R. A.; Pollack A. E.; Adler E. M.; Reppert S. M. (1992) Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: selective co-expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Mol. Brain Res. 14, 186–195. - PubMed
-
- Schiffmann S. N.; Lipert F.; Vassart G.; Vanderhaeghen J. J. (1991) Distribution of adenosine A2receptor mRNA in the human brain. Neurosci. Lett. 130, 177–181. - PubMed
-
- Olanow C. W. (1993) MAO-B inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Neurol. 60, 666–671. - PubMed
-
- Gordin A.; Brooks D. J. (2007) Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use of COMT inhibition in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 254, IV/37–IV/48.
- Olanow C. W.; Stocchi F. (2004) COMT inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Can they prevent and/or reverse levodopa-induced motor complications?. Neurology 62, S72–S81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

