Dopamine and serotonin modulate human GABAρ1 receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes
- PMID: 22860179
- PMCID: PMC3382461
- DOI: 10.1021/cn200083m
Dopamine and serotonin modulate human GABAρ1 receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes
Abstract
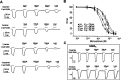
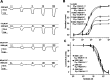
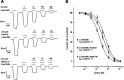
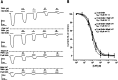
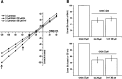
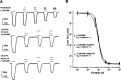
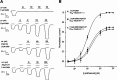
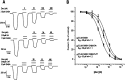
GABAρ1 receptors are highly expressed in bipolar neurons of the retina and to a lesser extent in several areas of the central nervous system (CNS), and dopamine and serotonin are also involved in the modulation of retinal neural transmission. Whether these biogenic amines have a direct effect on ionotropic GABA receptors was not known. Here, we report that GABAρ1 receptors, expressed in X. laevis oocytes, were negatively modulated by dopamine and serotonin and less so by octopamine and tyramine. Interestingly, these molecules did not have effects on GABA(A) receptors. 5-Carboxamido-tryptamine and apomorphine did not exert evident effects on any of the receptors. Schild plot analyses of the inhibitory actions of dopamine and serotonin on currents elicited by GABA showed slopes of 2.7 ± 0.3 and 6.1 ± 1.8, respectively, indicating a noncompetitive mechanism of inhibition. The inhibition of GABAρ1 currents was independent of the membrane potential and was insensitive to picrotoxin, a GABA receptor channel blocker and to the GABAρ-specific antagonist (1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-4-yl)methyl phosphinic acid (TPMPA). Dopamine and serotonin changed the sensitivity of GABAρ1 receptors to the inhibitory actions of Zn(2+). In contrast, La(3+) potentiated the amplitude of the GABA currents generated during negative modulation by dopamine (EC(50) 146 μM) and serotonin (EC(50) 196 μM). The functional role of the direct modulation of GABAρ receptors by dopamine and serotonin remains to be elucidated; however, it may represent an important modulatory pathway in the retina, where GABAρ receptors are highly expressed and where these biogenic amines are abundant.
Keywords: 5-HT; GABAA; GABAρ1; Xenopus oocyte; dopamine; receptor modulation.
Figures

References
-
- Cutting G. R.; Lu L.; O’Hara B. F.; Kash L. M.; Montrose-Refizadeh C.; Donovan D. M.; Shimada S.; Antonaraski S. E.; Guggino W. B.; Uhl G. R. (1991) Cloning of the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ρ1 cDNA: a GABA receptor subunit highly expressed in the retina. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 2673–2677. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woodward R. M.; Polenzani L.; Miledi R. (1992) Characterization of bicuculline/ baclofen-isensitive γ-aminobutyric acid expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Part I. Effect of Cl– channels inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 42, 165–173. - PubMed
-
- Woodward R. M.; Polenzani L.; Miledi R. (1993) Characterization of bicuculline/ baclofen-insensitive (ρ-like) γ-aminobutyric acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Part II. Pharmacology of γ-aminobutyric acid A and γ-aminobutyric acid B receptor agonists and antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 43, 609–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

