Transcriptomics analysis of lungs and peripheral blood of crystalline silica-exposed rats
- PMID: 22861000
- PMCID: PMC4672741
- DOI: 10.3109/08958378.2012.697926
Transcriptomics analysis of lungs and peripheral blood of crystalline silica-exposed rats
Abstract
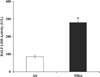
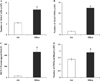
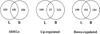
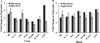
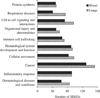
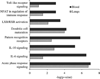
Minimally invasive approaches to detect/predict target organ toxicity have significant practical applications in occupational toxicology. The potential application of peripheral blood transcriptomics as a practical approach to study the mechanisms of silica-induced pulmonary toxicity was investigated. Rats were exposed by inhalation to crystalline silica (15 mg/m(3), 6 h/day, 5 days) and pulmonary toxicity and global gene expression profiles of lungs and peripheral blood were determined at 32 weeks following termination of exposure. A significant elevation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid lactate dehydrogenase activity and moderate histological changes in the lungs, including type II pneumocyte hyperplasia and fibrosis, indicated pulmonary toxicity in the rats. Similarly, significant infiltration of neutrophils and elevated monocyte chemotactic protein-1 levels in the lungs showed pulmonary inflammation in the rats. Microarray analysis of global gene expression profiles identified significant differential expression [>1.5-fold change and false discovery rate (FDR) p < 0.01] of 520 and 537 genes, respectively, in the lungs and blood of the exposed rats. Bioinformatics analysis of the differentially expressed genes demonstrated significant similarity in the biological processes, molecular networks, and canonical pathways enriched by silica exposure in the lungs and blood of the rats. Several genes involved in functions relevant to silica-induced pulmonary toxicity such as inflammation, respiratory diseases, cancer, cellular movement, fibrosis, etc, were found significantly differentially expressed in the lungs and blood of the silica-exposed rats. The results of this study suggested the potential application of peripheral blood gene expression profiling as a toxicologically relevant and minimally invasive surrogate approach to study the mechanisms underlying silica-induced pulmonary toxicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood transcriptomics: applications in toxicology.J Appl Toxicol. 2013 Nov;33(11):1193-202. doi: 10.1002/jat.2861. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Appl Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23456664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of pulmonary response progression in crystalline silica exposed rats.Inhal Toxicol. 2017 Feb;29(2):53-64. doi: 10.1080/08958378.2017.1282064. Epub 2017 Mar 19. Inhal Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28317464
-
Pulmonary toxicity and global gene expression changes in response to sub-chronic inhalation exposure to crystalline silica in rats.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017;80(23-24):1349-1368. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2017.1384773. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017. PMID: 29165057
-
Blood gene expression profiling detects silica exposure and toxicity.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Aug;122(2):253-64. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr125. Epub 2011 May 19. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21602193
-
Mechanisms of crystalline silica-induced pulmonary toxicity revealed by global gene expression profiling.Inhal Toxicol. 2011 Dec;23(14):927-37. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2011.625995. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Inhal Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 22087542 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of Chinese nickel refinery workers with high exposures to nickel and control subjects.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013 Feb;22(2):261-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1011. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013. PMID: 23195993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of TLR4 in silica-induced inflammation: An underlying mechanism of silicosis.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Jun 14;15(10):986-991. doi: 10.7150/ijms.24715. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30013439 Free PMC article.
-
Blood transcriptomics: applications in toxicology.J Appl Toxicol. 2013 Nov;33(11):1193-202. doi: 10.1002/jat.2861. Epub 2013 Mar 1. J Appl Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23456664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Silica Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Meta-Analysis.J Tehran Heart Cent. 2020 Oct;15(4):151-157. doi: 10.18502/jthc.v15i4.5940. J Tehran Heart Cent. 2020. PMID: 34178083 Free PMC article.
-
Results from omic approaches in rat or mouse models exposed to inhaled crystalline silica: a systematic review.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2024 Mar 1;21(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12989-024-00573-x. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38429797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Absher MP, Hemenway DR, Leslie KO, Trombley L, Vacek P. Intrathoracic distribution and transport of aerosolized silica in the rat. Exp Lung Res. 1992;18:743–757. - PubMed
-
- Antonini JM, Roberts JR. Chromium in stainless steel welding fume suppresses lung defense responses against bacterial infection in rats. J Immunotoxicol. 2007;4:117–127. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser. 1995;57:289–300.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
