Use of a blood gas analyzer and a laboratory autoanalyzer in routine practice to measure electrolytes in intensive care unit patients
- PMID: 22862792
- PMCID: PMC3431979
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2253-12-17
Use of a blood gas analyzer and a laboratory autoanalyzer in routine practice to measure electrolytes in intensive care unit patients
Abstract
Background: Electrolyte values are measured in most critically ill intensive care unit (ICU) patients using both an arterial blood gas analyzer (ABG) and a central laboratory auto-analyzer (AA). The aim of the present study was to investigate whether electrolyte levels assessed using an ABG and an AA were equivalent; data on sodium and potassium ion concentrations were examined.
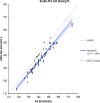
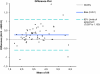
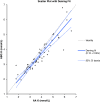
Methods: We retrospectively studied patients hospitalized in the ICU between July and August 2011. Of 1,105 test samples, we identified 84 instances of simultaneous sampling of arterial and venous blood, where both Na+ and K+ levels were measured using a pHOx Stat Profile Plus L blood gas analyzer (Nova Biomedical, Waltham MA, USA) and a Roche Modular P autoanalyzer (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Statistical measures employed to compare the data included Spearman's correlation coefficients, paired Student's t-tests, Deming regression analysis, and Bland-Altman plots.
Results: The mean sodium concentration was 138.1 mmol/L (SD 10.2 mmol/L) using the ABG and 143.0 mmol/L (SD 10.5) using the AA (p < 0.001). The mean potassium level was 3.5 mmol/L (SD 0.9 mmol/L) using the ABG and 3.7 mmol/L (SD 1.0 mmol/L) using the AA (p < 0.001). The extent of inter-analyzer agreement was unacceptable for both K+ and Na+, with biases of 0.150-0.352 and -0.97-10.05 respectively; the associated correlation coefficients were 0.88 and 0.90.
Conclusions: We conclude that the ABG and AA do not yield equivalent Na+ and K+ data. Concordance between ABG and AA should be established prior to introduction of new ABG systems.
Figures

References
-
- Murray MJ. Michael James, American Society of Critical Care Anesthesiologists. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA; 2002. 168; pp. 168–169.
-
- Eachempati SR. In: Critical Care Medicine. Porter RS, editor. The Merck Manuals. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc, Whitehouse Station, N.J., U.S.A; Approach to the Critically Ill Patient; pp. 2010–2011.
-
- Scott MG, LeGrys VA, Klutts JS. In: Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 4. Burtis DE, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE, editor. Elsevier, St Louis, MO; 2006. Electrolytes and blood gases; pp. 983–1018.
-
- D’Orazio P, Miller WG, Myers GL, Doumas BT, Eckfeldt JH, Evans SA, Graham GA, Parsons PJ, Stanton NV. Standardization of Sodium and Potassium Ion-Selective Electrode Systems to the Flame Photometric Reference Method; Approved Standard—Second Edition, C29-A2 [electronic document] CLSI. 2000;20:1–22.
-
- Ladenson JH. Direct potentiometric measurement of sodium and potassium in whole blood. Clin Chem. 1977;23(9):10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

