Tristetraprolin impairs myc-induced lymphoma and abolishes the malignant state
- PMID: 22863009
- PMCID: PMC3422762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.033
Tristetraprolin impairs myc-induced lymphoma and abolishes the malignant state
Abstract
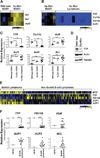
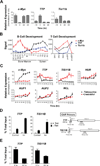
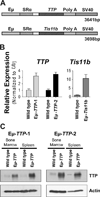
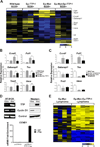
Myc oncoproteins directly regulate transcription by binding to target genes, yet this only explains a fraction of the genes affected by Myc. mRNA turnover is controlled via AU-binding proteins (AUBPs) that recognize AU-rich elements (AREs) found within many transcripts. Analyses of precancerous and malignant Myc-expressing B cells revealed that Myc regulates hundreds of ARE-containing (ARED) genes and select AUBPs. Notably, Myc directly suppresses transcription of Tristetraprolin (TTP/ZFP36), an mRNA-destabilizing AUBP, and this circuit is also operational during B lymphopoiesis and IL7 signaling. Importantly, TTP suppression is a hallmark of cancers with MYC involvement, and restoring TTP impairs Myc-induced lymphomagenesis and abolishes maintenance of the malignant state. Further, there is a selection for TTP loss in malignancy; thus, TTP functions as a tumor suppressor. Finally, Myc/TTP-directed control of select cancer-associated ARED genes is disabled during lymphomagenesis. Thus, Myc targets AUBPs to regulate ARED genes that control tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985;318:533–538. - PubMed
-
- Blackshear PJ. Tristetraprolin and other CCCH tandem zinc-finger proteins in the regulation of mRNA turnover. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002;30:945–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

