Homeodomain-containing protein HOXB9 regulates expression of growth and angiogenic factors, facilitates tumor growth in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer tissue
- PMID: 22863320
- PMCID: PMC3445661
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08733.x
Homeodomain-containing protein HOXB9 regulates expression of growth and angiogenic factors, facilitates tumor growth in vitro and is overexpressed in breast cancer tissue
Abstract
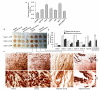
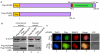
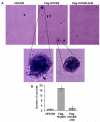
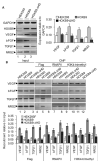
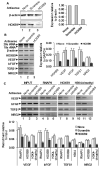
HOXB9 is a homeobox-containing gene and is critical for the development of mammary gland and sternum. HOXB9 is also regulated by estrogen and is critical for angiogenesis. We investigated the biochemical roles of HOXB9 and its homeodomain in cell-cycle progression and tumorigenesis. Our studies demonstrated that HOXB9 is overexpressed in breast cancer tissue. HOXB9 overexpression stimulated 3D formation in soft agar assay. HOXB9 binds to the promoters of various tumor growth and angiogenic factors and regulates their expression. The homeodomain of HOXB9 plays crucial roles in transcriptional regulation of tumor growth factors and also in 3D colony formation, indicating crucial roles of the HOXB9 homeodomain in tumorigenesis. Overall, we demonstrated that HOXB9 is a critical regulator of tumor growth factors and is associated with tumorigenesis.
© 2012 The Authors Journal compilation © 2012 FEBS.
Figures
References
-
- Zakany J, Duboule D. The role of Hox genes during vertebrate limb development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17:359–66. - PubMed
-
- Grier DG, Thompson A, Kwasniewska A, McGonigle GJ, Halliday HL, Lappin TR. The pathophysiology of HOX genes and their role in cancer. J Pathol. 2005;205:154–71. - PubMed
-
- Alexander T, Nolte C, Krumlauf R. Hox genes and segmentation of the hindbrain and axial skeleton. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:431–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

