DDR complex facilitates global association of RNA polymerase V to promoters and evolutionarily young transposons
- PMID: 22864289
- PMCID: PMC3443314
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2354
DDR complex facilitates global association of RNA polymerase V to promoters and evolutionarily young transposons
Abstract
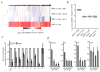
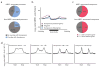
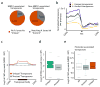
The plant-specific DNA-dependent RNA polymerase V (Pol V) evolved from Pol II to function in an RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway. Here, we have identified targets of Pol V in Arabidopsis thaliana on a genome-wide scale using ChIP-seq of NRPE1, the largest catalytic subunit of Pol V. We found that Pol V is enriched at promoters and evolutionarily recent transposons. This localization pattern is highly correlated with Pol V-dependent DNA methylation and small RNA accumulation. We also show that genome-wide chromatin association of Pol V is dependent on all members of a putative chromatin-remodeling complex termed DDR. Our study presents a genome-wide view of Pol V occupancy and sheds light on the mechanistic basis of Pol V localization. Furthermore, these findings suggest a role for Pol V and RNA-directed DNA methylation in genome surveillance and in responding to genome evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Epigenomics: dissecting the roles of Pol V.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Oct;13(10):673. doi: 10.1038/nrg3328. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22929988 No abstract available.
-
Pinpointing a puzzling polymerase.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;19(9):865-6. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2374. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22955933 No abstract available.
References
-
- Haag JR, Pikaard CS. Multisubunit RNA polymerases IV and V: purveyors of non-coding RNA for plant gene silencing. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2011;12:483–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

