Proteomic screen reveals Fbw7 as a modulator of the NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 22864569
- PMCID: PMC4354031
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1975
Proteomic screen reveals Fbw7 as a modulator of the NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Fbw7 is a ubiquitin-ligase that targets several oncoproteins for proteolysis, but the full range of Fbw7 substrates is not known. Here we show that by performing quantitative proteomics combined with degron motif searches, we effectively screened for a more complete set of Fbw7 targets. We identify 89 putative Fbw7 substrates, including several disease-associated proteins. The transcription factor NF-κB2 (p100/p52) is one of the candidate Fbw7 substrates. We show that Fbw7 interacts with p100 via a conserved degron and that it promotes degradation of p100 in a GSK3β phosphorylation-dependent manner. Fbw7 inactivation increases p100 levels, which in the presence of NF-κB pathway stimuli, leads to increased p52 levels and activity. Accordingly, the apoptotic threshold can be increased by loss of Fbw7 in a p100-dependent manner. In conclusion, Fbw7-mediated destruction of p100 is a regulatory component restricting the response to NF-κB2 pathway stimulation.
Figures
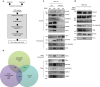
 RK
RK S/TP
S/TP RK
RK XS/T/E/D) and (3) proteins with motifs predicted to be phosphorylated by GSK3. (c) Validation of quantitative MS-data. WB analysis comparing endogenous protein levels in the different fractions from WT and KO cells. Equal protein amount from each cell type were analysed. (d) FBW7 KO cells were transiently transfected with Fbw7 and GSK-3β as indicated for 24 h. Whole cell extracts were analysed by WB.
XS/T/E/D) and (3) proteins with motifs predicted to be phosphorylated by GSK3. (c) Validation of quantitative MS-data. WB analysis comparing endogenous protein levels in the different fractions from WT and KO cells. Equal protein amount from each cell type were analysed. (d) FBW7 KO cells were transiently transfected with Fbw7 and GSK-3β as indicated for 24 h. Whole cell extracts were analysed by WB.
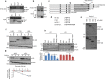


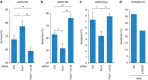
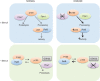
References
-
- Welcker M. & Clurman B. E. FBW7 ubiquitin ligase: a tumour suppressor at the crossroads of cell division, growth and differentiation. Nat. Rev. 8, 83–93 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Strohmaier H. et al.. Human F-box protein hCdc4 targets cyclin E for proteolysis and is mutated in a breast cancer cell line. Nature 413, 316–322 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Oberg C. et al.. The Notch intracellular domain is ubiquitinated and negatively regulated by the mammalian Sel-10 homolog. The Journal of biological chemistry 276, 35847–35853 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

