A fast and noise-resilient approach to detect rare-variant associations with deep sequencing data for complex disorders
- PMID: 22865616
- PMCID: PMC6240912
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21662
A fast and noise-resilient approach to detect rare-variant associations with deep sequencing data for complex disorders
Abstract
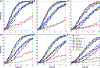
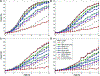
Next generation sequencing technology has enabled the paradigm shift in genetic association studies from the common disease/common variant to common disease/rare-variant hypothesis. Analyzing individual rare variants is known to be underpowered; therefore association methods have been developed that aggregate variants across a genetic region, which for exome sequencing is usually a gene. The foreseeable widespread use of whole genome sequencing poses new challenges in statistical analysis. It calls for new rare-variant association methods that are statistically powerful, robust against high levels of noise due to inclusion of noncausal variants, and yet computationally efficient. We propose a simple and powerful statistic that combines the disease-associated P-values of individual variants using a weight that is the inverse of the expected standard deviation of the allele frequencies under the null. This approach, dubbed as Sigma-P method, is extremely robust to the inclusion of a high proportion of noncausal variants and is also powerful when both detrimental and protective variants are present within a genetic region. The performance of the Sigma-P method was tested using simulated data based on realistic population demographic and disease models and its power was compared to several previously published methods. The results demonstrate that this method generally outperforms other rare-variant association methods over a wide range of models. Additionally, sequence data on the ANGPTL family of genes from the Dallas Heart Study were tested for associations with nine metabolic traits and both known and novel putative associations were uncovered using the Sigma-P method.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel adaptive method for the analysis of next-generation sequencing data to detect complex trait associations with rare variants due to gene main effects and interactions.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 14;6(10):e1001156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001156. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20976247 Free PMC article.
-
A power set-based statistical selection procedure to locate susceptible rare variants associated with complex traits with sequencing data.Bioinformatics. 2014 Aug 15;30(16):2317-23. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu207. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24755303
-
A weighted U-statistic for genetic association analyses of sequencing data.Genet Epidemiol. 2014 Dec;38(8):699-708. doi: 10.1002/gepi.21864. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Genet Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 25331574 Free PMC article.
-
Rare-variant genome-wide association studies: a new frontier in genetic analysis of complex traits.Pharmacogenomics. 2013 Mar;14(4):413-24. doi: 10.2217/pgs.13.36. Pharmacogenomics. 2013. PMID: 23438888 Review.
-
Statistical power and significance testing in large-scale genetic studies.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 May;15(5):335-46. doi: 10.1038/nrg3706. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24739678 Review.
Cited by
-
Association testing of clustered rare causal variants in case-control studies.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 15;9(4):e94337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094337. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24736372 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Group Testing Procedures for Analysis of High-Dimensional Genomic Data.Genomics Inform. 2016 Dec;14(4):187-195. doi: 10.5808/GI.2016.14.4.187. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Genomics Inform. 2016. PMID: 28154510 Free PMC article.
-
A powerful and adaptive association test for rare variants.Genetics. 2014 Aug;197(4):1081-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.165035. Epub 2014 May 15. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24831820 Free PMC article.
-
Variant association tools for quality control and analysis of large-scale sequence and genotyping array data.Am J Hum Genet. 2014 May 1;94(5):770-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.04.004. Am J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24791902 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting association of rare and common variants by adaptive combination of P-values.Genet Res (Camb). 2015 Oct 6;97:e20. doi: 10.1017/S0016672315000208. Genet Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26440553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahituv N, Kavaslar N, Schackwitz W, Ustaszewska A, Martin J, Hébert S, Doelle H, Ersoy B, Kryukov G, Schmidt S, Yosef N, Ruppin E, Sharan R, Vaisse C, Sunyaev S, Dent R, Cohen J, McPherson R, Pennacchio LA. 2007. Medical sequencing at the extremes of human body mass. Am J Hum Genet 80:779–791. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armitage P, Berry G, Matthews JNS. 2002. Statistical Methods in Medical Research (4th ed.) Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing.
-
- Barnard GA. 1989. On alleged gains in power from lower P-values. Stat Med 8:1469–1477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

