Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells cultured as spheroids are self-activated to produce prostaglandin E2 that directs stimulated macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype
- PMID: 22865689
- PMCID: PMC3448872
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.1191
Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells cultured as spheroids are self-activated to produce prostaglandin E2 that directs stimulated macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype
Abstract
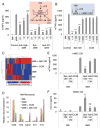
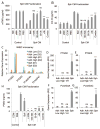
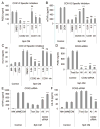
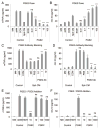
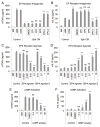
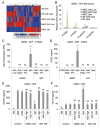
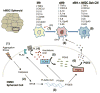
Culturing cells in three dimension (3D) provides an insight into their characteristics in vivo. We previously reported that human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (hMSCs) cultured as 3D spheroids acquire enhanced anti-inflammatory properties. Here, we explored the effects of hMSC spheroids on macrophages that are critical cells in the regulation of inflammation. Conditioned medium (CM) from hMSC spheroids inhibited lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages from secreting proinflammatory cytokines TNFα, CXCL2, IL6, IL12p40, and IL23. CM also increased the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL10 and IL1ra by the stimulated macrophages, and augmented expression of CD206, a marker of alternatively activated M2 macrophages. The principal anti-inflammatory activity in CM had a small molecular weight, and microarray data suggested that it was prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This was confirmed by the observations that PGE2 levels were markedly elevated in hMSC spheroid-CM, and that the anti-inflammatory activity was abolished by an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), a silencing RNA for COX-2, and an antibody to PGE2. The anti-inflammatory effects of the PGE2 on stimulated macrophages were mediated by the EP4 receptor. Spheroids formed by human adult dermal fibroblasts produced low levels of PGE2 and displayed negligible anti-inflammatory effects on stimulated macrophages, suggesting the features as unique to hMSCs. Moreover, production of PGE2 by hMSC spheroids was dependent on the activity of caspases and NFκB activation in the hMSCs. The results indicated that hMSCs in 3D-spheroid cultures are self-activated, in part by intracellular stress responses, to produce PGE2 that can change stimulated macrophages from a primarily proinflammatory M1 phenotype to a more anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype.
Copyright © 2012 AlphaMed Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multifactorial Experimental Design to Optimize the Anti-Inflammatory and Proangiogenic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids.Stem Cells. 2017 Jun;35(6):1493-1504. doi: 10.1002/stem.2606. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 28276602 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning of murine mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced immunomodulation and osteogenesis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Dec 6;8(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0730-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29212557 Free PMC article.
-
Human Mesenchymal stem cells program macrophage plasticity by altering their metabolic status via a PGE2-dependent mechanism.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 2;6:38308. doi: 10.1038/srep38308. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27910911 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammation therapy by activation of prostaglandin EP4 receptor in cardiovascular and other inflammatory diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;59(2):116-23. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182244a12. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21697732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of prostaglandin E2 in macrophage polarization: Insights into atherosclerosis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jan;207:115357. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115357. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36455672 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-inspired microgel scaffolds to control macrophage polarization.Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 Mar 21;6(2):e10217. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10217. eCollection 2021 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34027099 Free PMC article.
-
The promising roles of macrophages in geriatric hip fracture.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 26;10:962990. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.962990. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36092716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetrandrine identified in a small molecule screen to activate mesenchymal stem cells for enhanced immunomodulation.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 26;6:30263. doi: 10.1038/srep30263. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27457881 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials functionalized with MSC secreted extracellular vesicles and soluble factors for tissue regeneration.Adv Funct Mater. 2020 Sep 10;30(37):1909125. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909125. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Adv Funct Mater. 2020. PMID: 32952493 Free PMC article.
-
Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impact Th17 and Th1 Responses Through a Prostaglandin E2 and Myeloid-Dependent Mechanism.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Nov;5(11):1506-1514. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0243. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27400792 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

