mRNA localization and translational control in Drosophila oogenesis
- PMID: 22865893
- PMCID: PMC3475173
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012294
mRNA localization and translational control in Drosophila oogenesis
Abstract
Localization of an mRNA species to a particular subcellular region can complement translational control mechanisms to produce a restricted spatial distribution of the protein it encodes. mRNA localization has been studied most in asymmetric cells such as budding yeast, early embryos, and neurons, but the process is likely to be more widespread. This article reviews the current state of knowledge about the mechanisms of mRNA localization and its functions in early embryonic development, focusing on Drosophila where the relevant knowledge is most advanced. Links between mRNA localization and translational control mechanisms also are examined.
Figures
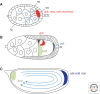
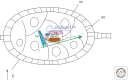
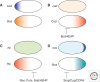
Similar articles
-
Localization, anchoring and translational control of oskar, gurken, bicoid and nanos mRNA during Drosophila oogenesis.Fly (Austin). 2009 Jan-Mar;3(1):15-28. doi: 10.4161/fly.3.1.7751. Epub 2009 Jan 2. Fly (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19182536 Review.
-
Translational regulation and RNA localization in Drosophila oocytes and embryos.Annu Rev Genet. 2001;35:365-406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.35.102401.090756. Annu Rev Genet. 2001. PMID: 11700288 Review.
-
Setting the stage for development: mRNA translation and stability during oocyte maturation and egg activation in Drosophila.Dev Dyn. 2005 Mar;232(3):593-608. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20297. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 15704150 Review.
-
Drosophila Ik2, a member of the I kappa B kinase family, is required for mRNA localization during oogenesis.Development. 2006 Apr;133(8):1467-75. doi: 10.1242/dev.02318. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Development. 2006. PMID: 16540511
-
Role of Adducin-like (hu-li tai shao) mRNA and protein localization in regulating cytoskeletal structure and function during Drosophila Oogenesis and early embryogenesis.Dev Genet. 1996;19(3):249-57. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1996)19:3<249::AID-DVG8>3.0.CO;2-9. Dev Genet. 1996. PMID: 8952067
Cited by
-
Optimal RNA binding by Egalitarian, a Dynein cargo adaptor, is critical for maintaining oocyte fate in Drosophila.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2376-2389. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1914422. Epub 2021 Apr 27. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33904382 Free PMC article.
-
Gatekeeper function for Short stop at the ring canals of the Drosophila ovary.Curr Biol. 2021 Aug 9;31(15):3207-3220.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34089646 Free PMC article.
-
Translational activation of oskar mRNA: reevaluation of the role and importance of a 5' regulatory element [corrected].PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0125849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125849. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938537 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct biogenesis pathways may have led to functional divergence of the human and Drosophila Arglu1 sisRNA.EMBO Rep. 2023 Feb 6;24(2):e54350. doi: 10.15252/embr.202154350. Epub 2022 Dec 19. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 36533631 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric distribution of biomolecules of maternal origin in the Xenopus laevis egg and their impact on the developmental plan.Sci Rep. 2018 May 29;8(1):8315. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26592-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29844480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnott S, Hukins DW, Dover SD 1972. Optimised parameters for RNA double-helices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 48: 1392–1399 - PubMed
-
- Bashirullah A, Halsell SR, Cooperstock RL, Kloc M, Karaiskakis A, Fisher WW, Fu W, Hamilton JK, Etkin LD, Lipshitz HD 1999. Joint action of two RNA degradation pathways controls the timing of maternal transcript elimination at the midblastula transition in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 18: 2610–2620 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastock R, St Johnston D 2008. Drosophila oogenesis. Curr Biol 18: R1082–R1087 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
