Ultrasonic colour Doppler imaging
- PMID: 22866227
- PMCID: PMC3262272
- DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0017
Ultrasonic colour Doppler imaging
Abstract
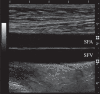
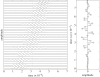
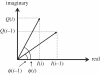
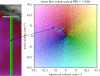
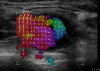
Ultrasonic colour Doppler is an imaging technique that combines anatomical information derived using ultrasonic pulse-echo techniques with velocity information derived using ultrasonic Doppler techniques to generate colour-coded maps of tissue velocity superimposed on grey-scale images of tissue anatomy. The most common use of the technique is to image the movement of blood through the heart, arteries and veins, but it may also be used to image the motion of solid tissues such as the heart walls. Colour Doppler imaging is now provided on almost all commercial ultrasound machines, and has been found to be of great value in assessing blood flow in many clinical conditions. Although the method for obtaining the velocity information is in many ways similar to the method for obtaining the anatomical information, it is technically more demanding for a number of reasons. It also has a number of weaknesses, perhaps the greatest being that in conventional systems, the velocities measured and thus displayed are the components of the flow velocity directly towards or away from the transducer, while ideally the method would give information about the magnitude and direction of the three-dimensional flow vectors. This review briefly introduces the principles behind colour Doppler imaging and describes some clinical applications. It then describes the basic components of conventional colour Doppler systems and the methods used to derive velocity information from the ultrasound signal. Next, a number of new techniques that seek to overcome the vector problem mentioned above are described. Finally, some examples of vector velocity images are presented.
Keywords: clinical applications; imaging; ultrasonic colour Doppler.
Figures





References
-
- Arning C., Widder B., von Reutern G. M., Stiegler H., ôrtler M. 2010. Revison of DEGUM ultrasound criteria for grading internal carotid artery stenoses and transfer to NASCET measurement. Ultraschall Med. 31, 251–25710.1055/s-0029-1245336 (doi:10.1055/s-0029-1245336) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Udesen J., Nielsen M. B., Nielsen K. R., Jensen J. A. 2007. Examples of in vivo blood vector velocity estimation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33, 541–54810.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.10.014 (doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2006.10.014) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thalhammer C., Aschwanden M., Mayr M., Staub D., Jaeger K. A. 2007. Colour-coded duplex sonography after renal transplantation. Ultraschall Med. 28, 6–2710.1055/s-2007-962859 (doi:10.1055/s-2007-962859) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jaeger K. A., Uthoff H. 2010. Is there still a place for renal artery duplex scanning? Ultraschall Med. 31, 339–34310.1055/s-0029-1245585 (doi:10.1055/s-0029-1245585) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamper U. M., Delong M. R., Scoutt L. M. 2009. Ultrasound evaluation of the lower extremity veins. Ultrasound Clin. 4, 193–21610.1016/j.cult.2009.04.003 (doi:10.1016/j.cult.2009.04.003) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
