Photoluminescence enhancement of quantum dots on Ag nanoneedles
- PMID: 22866992
- PMCID: PMC3466161
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-7-438
Photoluminescence enhancement of quantum dots on Ag nanoneedles
Abstract
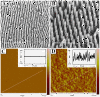
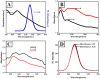
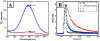
Noble metal nanostructure allows us to tune optical and electrical properties, which has high utility for real-world application. We studied surface plasmon-induced emission of semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) on engineered metallic nanostructures. Highly passive organic ZnS-capped CdSe QDs were spin-coated on poly-(methyl methacrylate)-covered Ag films, which brought QDs near the metallic surface. We obtained the enhanced electromagnetic field and reduced fluorescence lifetimes from CdSe/ZnS QDs due to the strong coupling of emitter wave function with the Ag plasmon resonance. Observed changes include a six-fold increase in the fluorescence intensity and striking reduction in fluorescence lifetimes of CdSe/ZnS QDs on rough Ag nanoneedle compared to the case of smooth surfaces. The advantages of using those nanocomposites are expected for high-efficiency light-emitting diodes, platform fabrication of biological and environmental monitoring, and high-contrast imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Chen S, Carroll DL. Synthesis and characterization of truncated triangular silver nanoplates. Nano Lett. 2002;2:1003. doi: 10.1021/nl025674h. - DOI
-
- Govorov AO, Bryant GW, Zhang W, Skeini T, Lee J, Kotov NA, Slocik JM, Naik RR. Exciton-plasmon interaction and hybrid excitons in semiconductor–metal nanoparticle assemblies. Nano Lett. 2006;6:984. doi: 10.1021/nl0602140. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

