Roles of CREB in the regulation of FMRP by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in cingulate cortex
- PMID: 22867433
- PMCID: PMC3478997
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-5-27
Roles of CREB in the regulation of FMRP by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in cingulate cortex
Abstract
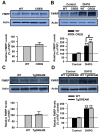
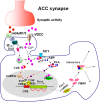
Background: Fragile X syndrome is caused by lack of fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) due to silencing of the FMR1 gene. The metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in the central nervous system contribute to higher brain functions including learning/memory, mental disorders and persistent pain. The transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) is involved in important neuronal functions, such as synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival. Our recent study has shown that stimulation of Group I mGluRs upregulated FMRP and activated CREB in anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), a key region for brain cognitive and executive functions, suggesting that activation of Group I mGluRs may upregulate FMRP through CREB signaling pathway.
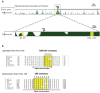
Results: In this study, we demonstrate that CREB contributes to the regulation of FMRP by Group I mGluRs. In ACC neurons of adult mice overexpressing dominant active CREB mutant, the upregulation of FMRP by stimulating Group I mGluR is enhanced compared to wild-type mice. However, the regulation of FMRP by Group I mGluRs is not altered by overexpression of Ca2+-insensitive mutant form of downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator (DREAM), a transcriptional repressor involved in synaptic transmission and plasticity.
Conclusion: Our study has provided further evidence for CREB involvement in regulation of FMRP by Group I mGluRs in ACC neurons, and may help to elucidate the pathogenesis of fragile X syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV links group I metabotropic glutamate receptors to fragile X mental retardation protein in cingulate cortex.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 10;284(28):18953-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.019141. Epub 2009 May 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19436069 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of calcium-stimulated adenylyl cyclase and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV in the regulation of FMRP by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors.J Neurosci. 2008 Apr 23;28(17):4385-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0646-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18434517 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a fragile X mental retardation protein-mediated translational switch in metabotropic glutamate receptor-triggered Arc translation and long-term depression.J Neurosci. 2012 Apr 25;32(17):5924-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4650-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22539853 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors and fragile x mental retardation protein: partners in translational regulation at the synapse.Sci Signal. 2008 Feb 5;1(5):pe6. doi: 10.1126/stke.15pe6. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 18272470 Review.
-
Fragile X syndrome: From protein function to therapy.Am J Med Genet A. 2013 Nov;161A(11):2809-21. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36241. Epub 2013 Sep 24. Am J Med Genet A. 2013. PMID: 24115651 Review.
Cited by
-
From Learning to Memory: What Flies Can Tell Us about Intellectual Disability Treatment.Front Psychiatry. 2015 Jun 3;6:85. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00085. eCollection 2015. Front Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26089803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Ethanol Produces Ataxia and Induces Fmr1 Expression via Histone Modifications in the Rat Cerebellum.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Jun;43(6):1191-1198. doi: 10.1111/acer.14044. Epub 2019 May 14. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 30969437 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term potentiation in the anterior cingulate cortex and chronic pain.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 2;369(1633):20130146. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0146. Print 2014 Jan 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24298148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic association of FMRP targets with psychiatric disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;26(7):2977-2990. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-00912-2. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33077856 Free PMC article.
-
FMRP S499 is phosphorylated independent of mTORC1-S6K1 activity.PLoS One. 2014 May 7;9(5):e96956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096956. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24806451 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

