Preclinical Profile and Characterization of the Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
- PMID: 22869577
- PMCID: PMC3457370
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01186-12
Preclinical Profile and Characterization of the Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Abstract
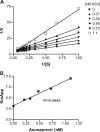
Asunaprevir (ASV; BMS-650032) is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 protease inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy in patients chronically infected with HCV genotype 1 when combined with alfa interferon and/or the NS5A replication complex inhibitor daclatasvir. ASV competitively binds to the NS3/4A protease complex, with K(i) values of 0.4 and 0.24 nM against recombinant enzymes representing genotypes 1a (H77) and 1b (J4L6S), respectively. Selectivity was demonstrated by the absence of any significant activity against the closely related GB virus-B NS3 protease and a panel of human serine or cysteine proteases. In cell culture, ASV inhibited replication of HCV replicons representing genotypes 1 and 4, with 50% effective concentrations (EC(50)s) ranging from 1 to 4 nM, and had weaker activity against genotypes 2 and 3 (EC(50), 67 to 1,162 nM). Selectivity was again demonstrated by the absence of activity (EC(50), >12 μM) against a panel of other RNA viruses. ASV exhibited additive or synergistic activity in combination studies with alfa interferon, ribavirin, and/or inhibitors specifically targeting NS5A or NS5B. Plasma and tissue exposures in vivo in several animal species indicated that ASV displayed a hepatotropic disposition (liver-to-plasma ratios ranging from 40- to 359-fold across species). Twenty-four hours postdose, liver exposures across all species tested were ≥110-fold above the inhibitor EC(50)s observed with HCV genotype-1 replicons. Based on these virologic and exposure properties, ASV holds promise for future utility in a combination with other anti-HCV agents in the treatment of HCV-infected patients.
Figures

References
-
- Bartenschlager R. 1999. The NS3/4A proteinase of the hepatitis C virus: unravelling structure and function of an unusual enzyme and a prime target for antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 6:165–181 - PubMed
-
- Reference deleted.
-
- Bronowicki J-P, et al. 2012. Asunaprevir (ASV; BMS-650032), an NS3 protease inhibitor, in combination with peginterferon and ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C infection. J. Hepatol. 56(Suppl 2):S431–S432
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

